diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 2477f2c..440082c 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -1,7 +1,14 @@
-
-
Linux 教程
-
+
+
+  +
+
+
+
+
+  +
+
+
+Linux Tutorial
> 🔁 项目同步维护在 [github](https://github.com/dunwu/linux-tutorial) | [gitee](https://gitee.com/turnon/linux-tutorial)
>
> 📖 [电子书](https://dunwu.github.io/linux-tutorial/) | [电子书(国内)](http://turnon.gitee.io/linux-tutorial/)
@@ -16,25 +23,26 @@
> 学习 Linux 的第一步:当然是从 [Linux 命令](docs/linux/cli/README.md) 入手了。
-- [查看 Linux 命令帮助信息](docs/linux/cli/查看Linux命令帮助信息.md)
-- [Linux 文件目录管理](docs/linux/cli/Linux文件目录管理.md)
-- [Linux 文件内容查看命令](docs/linux/cli/Linux文件内容查看编辑.md)
-- [Linux 文件压缩和解压](docs/linux/cli/Linux文件压缩和解压.md)
-- [Linux 用户管理](docs/linux/cli/Linux用户管理.md)
-- [Linux 系统管理](docs/linux/cli/Linux系统管理.md)
-- [Linux 网络管理](docs/linux/cli/Linux网络管理.md)
-- [Linux 硬件管理](docs/linux/cli/Linux硬件管理.md)
-- [Linux 软件管理](docs/linux/cli/Linux硬件管理.md)
+- [查看 Linux 命令帮助信息](docs/linux/cli/查看Linux命令帮助信息.md) - 关键词:`help`, `whatis`, `info`, `which`, `whereis`, `man`
+- [Linux 文件目录管理](docs/linux/cli/Linux文件目录管理.md) - 关键词:`cd`, `ls`, `pwd`, `mkdir`, `rmdir`, `tree`, `touch`, `ln`, `rename`, `stat`, `file`, `chmod`, `chown`, `locate`, `find`, `cp`, `mv`, `rm`
+- [Linux 文件内容查看命令](docs/linux/cli/Linux文件内容查看编辑.md) - 关键词:`cat`, `head`, `tail`, `more`, `less`, `sed`, `vi`, `grep`
+- [Linux 文件压缩和解压](docs/linux/cli/Linux文件压缩和解压.md) - 关键词:`tar`, `gzip`, `zip`, `unzip`
+- [Linux 用户管理](docs/linux/cli/Linux用户管理.md) - 关键词:`groupadd`, `groupdel`, `groupmod`, `useradd`, `userdel`, `usermod`, `passwd`, `su`, `sudo`
+- [Linux 系统管理](docs/linux/cli/Linux系统管理.md) - 关键词:`reboot`, `exit`, `shutdown`, `date`, `mount`, `umount`, `ps`, `kill`, `systemctl`, `service`, `crontab`
+- [Linux 网络管理](docs/linux/cli/Linux网络管理.md) - 关键词:关键词:`curl`, `wget`, `telnet`, `ip`, `hostname`, `ifconfig`, `route`, `ssh`, `ssh-keygen`, `firewalld`, `iptables`, `host`, `nslookup`, `nc`/`netcat`, `ping`, `traceroute`, `netstat`
+- [Linux 硬件管理](docs/linux/cli/Linux硬件管理.md) - 关键词:`df`, `du`, `top`, `free`, `iotop`
+- [Linux 软件管理](docs/linux/cli/Linux硬件管理.md) - 关键词:`rpm`, `yum`, `apt-get`
### Linux 系统运维
> Linux 系统的常见运维工作。
-- [linux 典型运维应用](linux/ops/linux典型运维应用.md)
-- [samba 使用详解](linux/ops/samba使用详解.md)
-- [Systemd 教程](linux/ops/systemd.md)
-- [Vim 应用指南](linux/ops/vim.md)
-- [Zsh 应用指南](linux/ops/zsh.md)
+- [linux 典型运维应用](docs/linux/ops/linux典型运维应用.md) - 关键词:域名解析、防火墙、网卡、NTP、crontab
+- [Samba 应用](docs/linux/ops/samba.md)
+- [Systemd 应用](docs/linux/ops/systemd.md)
+- [Vim 应用](docs/linux/ops/vim.md)
+- [Iptables 应用](docs/linux/ops/iptables.md)
+- [oh-my-zsh 应用](docs/linux/ops/zsh.md)
### 软件运维
@@ -91,8 +99,9 @@
## 资源
- **Linux 命令**
- - [Linux 命令大全](http://man.linuxde.net/)
- - [linux-command](https://jaywcjlove.gitee.io/linux-command/)
+ - [命令行的艺术](https://github.com/jlevy/the-art-of-command-line/blob/master/README-zh.md)
+ - [Linux 命令大全](https://man.linuxde.net/)
+ - [linux-command](https://github.com/jaywcjlove/linux-command)
- **社区网站**
- [Linux 中国](https://linux.cn/) - 各种资讯、文章、技术
- [实验楼](https://www.shiyanlou.com/) - 免费提供了 Linux 在线环境,不用在自己机子上装系统也可以学习 Linux,超方便实用。
diff --git a/docs/README.md b/docs/README.md
index c3bec26..ff8f6a5 100644
--- a/docs/README.md
+++ b/docs/README.md
@@ -1,6 +1,14 @@
-
-
Linux 教程
-
+
+
+  +
+
+
+
+
+
+  +
+
+
+Linux Tutorial
> 🔁 项目同步维护在 [github](https://github.com/dunwu/linux-tutorial) | [gitee](https://gitee.com/turnon/linux-tutorial)
>
@@ -16,22 +24,22 @@
> 学习 Linux 的第一步:当然是从 [Linux 命令](linux/cli/README.md) 入手了。
-- [查看 Linux 命令帮助信息](linux/cli/查看Linux命令帮助信息.md)
-- [Linux 文件目录管理](linux/cli/Linux文件目录管理.md)
-- [Linux 文件内容查看命令](linux/cli/Linux文件内容查看编辑.md)
-- [Linux 文件压缩和解压](linux/cli/Linux文件压缩和解压.md)
-- [Linux 用户管理](linux/cli/Linux用户管理.md)
-- [Linux 系统管理](linux/cli/Linux系统管理.md)
-- [Linux 网络管理](linux/cli/Linux网络管理.md)
-- [Linux 硬件管理](linux/cli/Linux硬件管理.md)
-- [Linux 软件管理](linux/cli/Linux硬件管理.md)
+- [查看 Linux 命令帮助信息](linux/cli/查看Linux命令帮助信息.md) - 关键词:`help`, `whatis`, `info`, `which`, `whereis`, `man`
+- [Linux 文件目录管理](linux/cli/Linux文件目录管理.md) - 关键词:`cd`, `ls`, `pwd`, `mkdir`, `rmdir`, `tree`, `touch`, `ln`, `rename`, `stat`, `file`, `chmod`, `chown`, `locate`, `find`, `cp`, `mv`, `rm`
+- [Linux 文件内容查看命令](linux/cli/Linux文件内容查看编辑.md) - 关键词:`cat`, `head`, `tail`, `more`, `less`, `sed`, `vi`, `grep`
+- [Linux 文件压缩和解压](linux/cli/Linux文件压缩和解压.md) - 关键词:`tar`, `gzip`, `zip`, `unzip`
+- [Linux 用户管理](linux/cli/Linux用户管理.md) - 关键词:`groupadd`, `groupdel`, `groupmod`, `useradd`, `userdel`, `usermod`, `passwd`, `su`, `sudo`
+- [Linux 系统管理](linux/cli/Linux系统管理.md) - 关键词:`reboot`, `exit`, `shutdown`, `date`, `mount`, `umount`, `ps`, `kill`, `systemctl`, `service`, `crontab`
+- [Linux 网络管理](linux/cli/Linux网络管理.md) - 关键词:关键词:`curl`, `wget`, `telnet`, `ip`, `hostname`, `ifconfig`, `route`, `ssh`, `ssh-keygen`, `firewalld`, `iptables`, `host`, `nslookup`, `nc`/`netcat`, `ping`, `traceroute`, `netstat`
+- [Linux 硬件管理](linux/cli/Linux硬件管理.md) - 关键词:`df`, `du`, `top`, `free`, `iotop`
+- [Linux 软件管理](linux/cli/Linux硬件管理.md) - 关键词:`rpm`, `yum`, `apt-get`
### Linux 系统运维
> Linux 系统的常见运维工作。
- [linux 典型运维应用](linux/ops/linux典型运维应用.md)
-- [samba 使用详解](linux/ops/samba使用详解.md)
+- [samba 使用详解](linux/ops/samba.md)
- [Systemd 教程](linux/ops/systemd.md)
- [Vim 应用指南](linux/ops/vim.md)
- [Zsh 应用指南](linux/ops/zsh.md)
@@ -91,8 +99,9 @@
## 资源
- **Linux 命令**
- - [Linux 命令大全](http://man.linuxde.net/)
- - [linux-command](https://jaywcjlove.gitee.io/linux-command/)
+ - [命令行的艺术](https://github.com/jlevy/the-art-of-command-line/blob/master/README-zh.md)
+ - [Linux命令大全](https://man.linuxde.net/)
+ - [linux-command](https://github.com/jaywcjlove/linux-command)
- **社区网站**
- [Linux 中国](https://linux.cn/) - 各种资讯、文章、技术
- [实验楼](https://www.shiyanlou.com/) - 免费提供了 Linux 在线环境,不用在自己机子上装系统也可以学习 Linux,超方便实用。
diff --git a/docs/index.html b/docs/index.html
index 77b43de..66adae3 100644
--- a/docs/index.html
+++ b/docs/index.html
@@ -169,7 +169,6 @@
}
.markdown-section p {
- line-height: 1rem;
word-spacing: 0.05rem;
}
diff --git a/docs/linux/cli/Linux文件目录管理.md b/docs/linux/cli/Linux文件目录管理.md
index 56b5d64..2ff7f15 100644
--- a/docs/linux/cli/Linux文件目录管理.md
+++ b/docs/linux/cli/Linux文件目录管理.md
@@ -8,7 +8,7 @@
linux 目录结构是树形结构,其根目录是 `/` 。一张思维导图说明各个目录的作用:
-

+
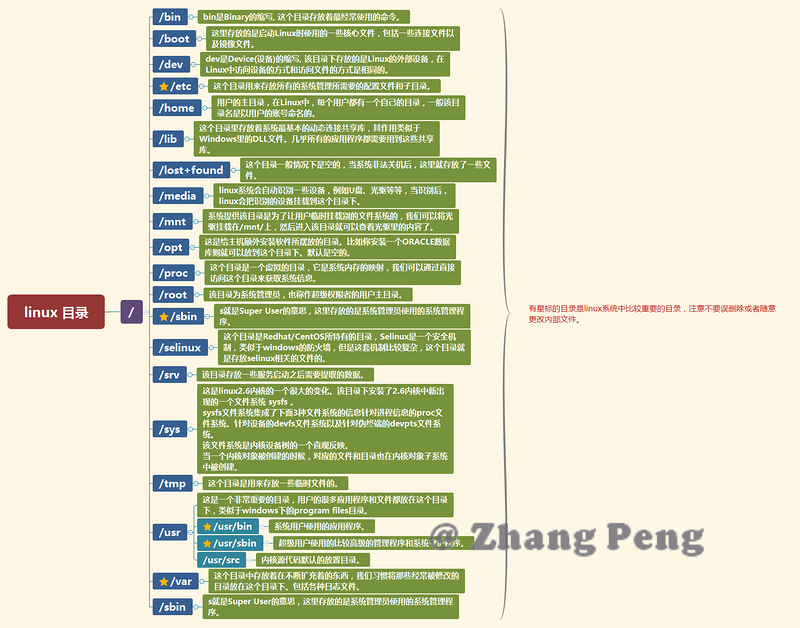
### 1.2. Linux 文件属性
diff --git a/docs/linux/cli/README.md b/docs/linux/cli/README.md
index d3a1973..41442c4 100644
--- a/docs/linux/cli/README.md
+++ b/docs/linux/cli/README.md
@@ -1,10 +1,6 @@
# Linux 命令行
-## :memo: 知识点
-
-> 根据应用场景,将常见 Linux 命令分门别类的一一介绍。
->
-> 如果想快速学习,推荐参考这篇文章:[命令行的艺术(转载)](命令行的艺术.md)
+## 常用命令
- [查看 Linux 命令帮助信息](查看Linux命令帮助信息.md) - 关键词:`help`, `whatis`, `info`, `which`, `whereis`, `man`
- [Linux 文件目录管理](Linux文件目录管理.md) - 关键词:`cd`, `ls`, `pwd`, `mkdir`, `rmdir`, `tree`, `touch`, `ln`, `rename`, `stat`, `file`, `chmod`, `chown`, `locate`, `find`, `cp`, `mv`, `rm`
@@ -15,3 +11,10 @@
- [Linux 网络管理](Linux网络管理.md) - 关键词:关键词:`curl`, `wget`, `telnet`, `ip`, `hostname`, `ifconfig`, `route`, `ssh`, `ssh-keygen`, `firewalld`, `iptables`, `host`, `nslookup`, `nc`/`netcat`, `ping`, `traceroute`, `netstat`
- [Linux 硬件管理](Linux硬件管理.md) - 关键词:`df`, `du`, `top`, `free`, `iotop`
- [Linux 软件管理](Linux硬件管理.md) - 关键词:`rpm`, `yum`, `apt-get`
+
+## 资料
+
+- [命令行的艺术](https://github.com/jlevy/the-art-of-command-line/blob/master/README-zh.md)
+- [Linux命令大全](https://man.linuxde.net/)
+- [linux-command](https://github.com/jaywcjlove/linux-command)
+
diff --git a/docs/linux/ops/README.md b/docs/linux/ops/README.md
index ea47db1..e28138a 100644
--- a/docs/linux/ops/README.md
+++ b/docs/linux/ops/README.md
@@ -1,3 +1,3 @@
- [linux 典型运维应用](linux典型运维应用.md)
-- [samba 使用详解](samba使用详解.md)
+- [samba 使用详解](samba.md)
diff --git a/docs/linux/ops/iptables.md b/docs/linux/ops/iptables.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..4863c05
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/linux/ops/iptables.md
@@ -0,0 +1,279 @@
+# Iptables 应用
+
+> _iptables_ 是一个配置 Linux 内核 [防火墙](https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/Firewall) 的命令行工具,是 [netfilter](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Netfilter) 项目的一部分。 可以直接配置,也可以通过许多前端和图形界面配置。
+>
+> iptables 也经常代指该内核级防火墙。iptables 用于 [ipv4](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ipv4),_ip6tables_ 用于 [ipv6](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ipv6)。
+>
+> [nftables](https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/Nftables) 已经包含在 [Linux kernel 3.13](http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=MTQ5MDU) 中,以后会取代 iptables 成为主要的 Linux 防火墙工具。
+>
+> 环境:CentOS7
+
+## 1. 简介
+
+**iptables 可以检测、修改、转发、重定向和丢弃 IPv4 数据包**。
+
+过滤 IPv4 数据包的代码已经内置于内核中,并且按照不同的目的被组织成 **表** 的集合。**表** 由一组预先定义的 **链** 组成,**链**包含遍历顺序规则。每一条规则包含一个谓词的潜在匹配和相应的动作(称为 **目标**),如果谓词为真,该动作会被执行。也就是说条件匹配。
+
+## 2. 安装 iptables
+
+(1)禁用 firewalld
+
+CentOS 7 上默认安装了 firewalld 作为防火墙,使用 iptables 建议关闭并禁用 firewalld。
+
+```bash
+systemctl stop firewalld
+systemctl disable firewalld
+```
+
+(2)安装 iptables
+
+```
+yum install -y iptables-services
+```
+
+(3)服务管理
+
+- 查看服务状态:`systemctl status iptables`
+- 启用服务:`systemctl enable iptables`
+- 禁用服务:`systemctl disable iptables`
+- 启动服务:`systemctl start iptables`
+- 重启服务:`systemctl restart iptables`
+- 关闭服务: `systemctl stop iptables`
+
+## 3. 命令
+
+基本语法:
+
+```
+iptables(选项)(参数)
+```
+
+基本选项说明:
+
+| 参数 | 作用 |
+| ----------- | ------------------------------------------------- |
+| -P | 设置默认策略:iptables -P INPUT (DROP |
+| -F | 清空规则链 |
+| -L | 查看规则链 |
+| -A | 在规则链的末尾加入新规则 |
+| -I | num 在规则链的头部加入新规则 |
+| -D | num 删除某一条规则 |
+| -s | 匹配来源地址 IP/MASK,加叹号"!"表示除这个 IP 外。 |
+| -d | 匹配目标地址 |
+| -i | 网卡名称 匹配从这块网卡流入的数据 |
+| -o | 网卡名称 匹配从这块网卡流出的数据 |
+| -p | 匹配协议,如 tcp,udp,icmp |
+| --dport num | 匹配目标端口号 |
+| --sport num | 匹配来源端口号 |
+
+顺序:
+
+```
+iptables -t 表名 <-A/I/D/R> 规则链名 [规则号] <-i/o 网卡名> -p 协议名 <-s 源IP/源子网> --sport 源端口 <-d 目标IP/目标子网> --dport 目标端口 -j 动作
+```
+
+## 4. iptables 示例
+
+### 4.1. 清空当前的所有规则和计数
+
+```shell
+iptables -F # 清空所有的防火墙规则
+iptables -X # 删除用户自定义的空链
+iptables -Z # 清空计数
+```
+
+### 4.2. 配置允许 ssh 端口连接
+
+```shell
+iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.1.0/24 -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
+# 22为你的ssh端口, -s 192.168.1.0/24表示允许这个网段的机器来连接,其它网段的ip地址是登陆不了你的机器的。 -j ACCEPT表示接受这样的请求
+```
+
+### 4.3. 允许本地回环地址可以正常使用
+
+```shell
+iptables -A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT
+#本地圆环地址就是那个127.0.0.1,是本机上使用的,它进与出都设置为允许
+iptables -A OUTPUT -o lo -j ACCEPT
+```
+
+### 4.4. 设置默认的规则
+
+```shell
+iptables -P INPUT DROP # 配置默认的不让进
+iptables -P FORWARD DROP # 默认的不允许转发
+iptables -P OUTPUT ACCEPT # 默认的可以出去
+```
+
+### 4.5. 配置白名单
+
+```shell
+iptables -A INPUT -p all -s 192.168.1.0/24 -j ACCEPT # 允许机房内网机器可以访问
+iptables -A INPUT -p all -s 192.168.140.0/24 -j ACCEPT # 允许机房内网机器可以访问
+iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -s 183.121.3.7 --dport 3380 -j ACCEPT # 允许183.121.3.7访问本机的3380端口
+```
+
+### 4.6. 开启相应的服务端口
+
+```shell
+iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT # 开启80端口,因为web对外都是这个端口
+iptables -A INPUT -p icmp --icmp-type 8 -j ACCEPT # 允许被ping
+iptables -A INPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT # 已经建立的连接得让它进来
+```
+
+### 4.7. 保存规则到配置文件中
+
+```shell
+cp /etc/sysconfig/iptables /etc/sysconfig/iptables.bak # 任何改动之前先备份,请保持这一优秀的习惯
+iptables-save > /etc/sysconfig/iptables
+cat /etc/sysconfig/iptables
+```
+
+### 4.8. 列出已设置的规则
+
+> iptables -L [-t 表名][链名]
+
+- 四个表名 `raw`,`nat`,`filter`,`mangle`
+- 五个规则链名 `INPUT`、`OUTPUT`、`FORWARD`、`PREROUTING`、`POSTROUTING`
+- filter 表包含`INPUT`、`OUTPUT`、`FORWARD`三个规则链
+
+```shell
+iptables -L -t nat # 列出 nat 上面的所有规则
+# ^ -t 参数指定,必须是 raw, nat,filter,mangle 中的一个
+iptables -L -t nat --line-numbers # 规则带编号
+iptables -L INPUT
+
+iptables -L -nv # 查看,这个列表看起来更详细
+```
+
+### 4.9. 清除已有规则
+
+```shell
+iptables -F INPUT # 清空指定链 INPUT 上面的所有规则
+iptables -X INPUT # 删除指定的链,这个链必须没有被其它任何规则引用,而且这条上必须没有任何规则。
+ # 如果没有指定链名,则会删除该表中所有非内置的链。
+iptables -Z INPUT # 把指定链,或者表中的所有链上的所有计数器清零。
+```
+
+### 4.10. 删除已添加的规则
+
+```shell
+# 添加一条规则
+iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.1.5 -j DROP
+```
+
+将所有 iptables 以序号标记显示,执行:
+
+```shell
+iptables -L -n --line-numbers
+```
+
+比如要删除 INPUT 里序号为 8 的规则,执行:
+
+```shell
+iptables -D INPUT 8
+```
+
+### 4.11. 开放指定的端口
+
+```shell
+iptables -A INPUT -s 127.0.0.1 -d 127.0.0.1 -j ACCEPT #允许本地回环接口(即运行本机访问本机)
+iptables -A INPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT #允许已建立的或相关连的通行
+iptables -A OUTPUT -j ACCEPT #允许所有本机向外的访问
+iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT #允许访问22端口
+iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT #允许访问80端口
+iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 21 -j ACCEPT #允许ftp服务的21端口
+iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 20 -j ACCEPT #允许FTP服务的20端口
+iptables -A INPUT -j reject #禁止其他未允许的规则访问
+iptables -A FORWARD -j REJECT #禁止其他未允许的规则访问
+```
+
+### 4.12. 屏蔽 IP
+
+```shell
+iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp -s 192.168.0.8 -j DROP # 屏蔽恶意主机(比如,192.168.0.8
+iptables -I INPUT -s 123.45.6.7 -j DROP #屏蔽单个IP的命令
+iptables -I INPUT -s 123.0.0.0/8 -j DROP #封整个段即从123.0.0.1到123.255.255.254的命令
+iptables -I INPUT -s 124.45.0.0/16 -j DROP #封IP段即从123.45.0.1到123.45.255.254的命令
+iptables -I INPUT -s 123.45.6.0/24 -j DROP #封IP段即从123.45.6.1到123.45.6.254的命令是
+```
+
+### 4.13. 指定数据包出去的网络接口
+
+只对 OUTPUT,FORWARD,POSTROUTING 三个链起作用。
+
+```shell
+iptables -A FORWARD -o eth0
+```
+
+### 4.14. 查看已添加的规则
+
+```shell
+iptables -L -n -v
+Chain INPUT (policy DROP 48106 packets, 2690K bytes)
+ pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
+ 5075 589K ACCEPT all -- lo * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
+ 191K 90M ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:22
+1499K 133M ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:80
+4364K 6351M ACCEPT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state RELATED,ESTABLISHED
+ 6256 327K ACCEPT icmp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
+
+Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
+ pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
+
+Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 3382K packets, 1819M bytes)
+ pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
+ 5075 589K ACCEPT all -- * lo 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
+```
+
+### 4.15. 启动网络转发规则
+
+公网`210.14.67.7`让内网`192.168.188.0/24`上网
+
+```shell
+iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.188.0/24 -j SNAT --to-source 210.14.67.127
+```
+
+### 4.16. 端口映射
+
+本机的 2222 端口映射到内网 虚拟机的 22 端口
+
+```shell
+iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -d 210.14.67.127 -p tcp --dport 2222 -j DNAT --to-dest 192.168.188.115:22
+```
+
+### 4.17. 字符串匹配
+
+比如,我们要过滤所有 TCP 连接中的字符串`test`,一旦出现它我们就终止这个连接,我们可以这么做:
+
+```shell
+iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m string --algo kmp --string "test" -j REJECT --reject-with tcp-reset
+iptables -L
+
+# Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
+# target prot opt source destination
+# REJECT tcp -- anywhere anywhere STRING match "test" ALGO name kmp TO 65535 reject-with tcp-reset
+#
+# Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT)
+# target prot opt source destination
+#
+# Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
+# target prot opt source destination
+```
+
+### 4.18. 阻止 Windows 蠕虫的攻击
+
+```shell
+iptables -I INPUT -j DROP -p tcp -s 0.0.0.0/0 -m string --algo kmp --string "cmd.exe"
+```
+
+### 4.19. 防止 SYN 洪水攻击
+
+```shell
+iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --syn -m limit --limit 5/second -j ACCEPT
+```
+
+## 5. 参考资料
+
+- https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/iptables_(%E7%AE%80%E4%BD%93%E4%B8%AD%E6%96%87)
+- https://wangchujiang.com/linux-command/c/iptables.html
diff --git a/docs/linux/ops/linux典型运维应用.md b/docs/linux/ops/linux典型运维应用.md
index 5c33727..d4596d9 100644
--- a/docs/linux/ops/linux典型运维应用.md
+++ b/docs/linux/ops/linux典型运维应用.md
@@ -83,6 +83,37 @@ systemctl 是 CentOS7 的服务管理工具中主要的工具,它融合之前
> :point_right: 参考:[CentOS7 使用 firewalld 打开关闭防火墙与端口](https://www.cnblogs.com/moxiaoan/p/5683743.html)
+### 1.3. 配置网卡
+
+使用 root 权限编辑 `/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eno16777736X` 文件
+
+参考以下进行配置:
+
+```properties
+TYPE=Ethernet # 网络类型:Ethernet以太网
+BOOTPROTO=none # 引导协议:自动获取、static静态、none不指定
+DEFROUTE=yes # 启动默认路由
+IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no # 不启用IPV4错误检测功能
+IPV6INIT=yes # 启用IPV6协议
+IPV6_AUTOCONF=yes # 自动配置IPV6地址
+IPV6_DEFROUTE=yes # 启用IPV6默认路由
+IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL=no # 不启用IPV6错误检测功能
+IPV6_PEERDNS=yes
+IPV6_PEERROUTES=yes
+IPV6_PRIVACY="no"
+
+NAME=eno16777736 # 网卡设备的别名(需要和文件名同名)
+UUID=90528772-9967-46da-b401-f82b64b4acbc # 网卡设备的UUID唯一标识号
+DEVICE=eno16777736 # 网卡的设备名称
+ONBOOT=yes # 开机自动激活网卡
+IPADDR=192.168.1.199 # 网卡的固定IP地址
+PREFIX=24 # 子网掩码
+GATEWAY=192.168.1.1 # 默认网关IP地址
+DNS1=8.8.8.8 # DNS域名解析服务器的IP地址
+```
+
+修改完后,执行 `systemctl restart network.service` 重启网卡服务。
+
## 2. 系统维护
### 2.1. 使用 NTP 进行时间同步
diff --git a/docs/linux/ops/samba使用详解.md b/docs/linux/ops/samba.md
similarity index 99%
rename from docs/linux/ops/samba使用详解.md
rename to docs/linux/ops/samba.md
index e7319ea..116ddc1 100644
--- a/docs/linux/ops/samba使用详解.md
+++ b/docs/linux/ops/samba.md
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-# samba 使用详解
+# Samba 应用
> samba 是在 Linux 和 UNIX 系统上实现 SMB 协议的一个免费软件。
>
diff --git a/docs/linux/ops/systemd.md b/docs/linux/ops/systemd.md
index fa95e91..a7f9d73 100644
--- a/docs/linux/ops/systemd.md
+++ b/docs/linux/ops/systemd.md
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-# Systemd 教程
+# Systemd 应用
> 搬运自:[Systemd 入门教程:命令篇](http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2016/03/systemd-tutorial-commands.html)、[Systemd 入门教程:实战篇](hhttp://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2016/03/systemd-tutorial-part-two.html)
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ Systemd 是 Linux 系统工具,用来启动[守护进程](http://www.ruanyifen
本文介绍它的基本用法,分为上下两篇。今天介绍它的主要命令,[下一篇](http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2016/03/systemd-tutorial-part-two.html)介绍如何用于实战。
-## 由来
+## 1. 由来
历史上,[Linux 的启动](http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2013/08/linux_boot_process.html)一直采用[`init`](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Init)进程。
@@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ $ service apache2 start
二是启动脚本复杂。`init`进程只是执行启动脚本,不管其他事情。脚本需要自己处理各种
情况,这往往使得脚本变得很长。
-## Systemd 概述
+## 2. Systemd 概述
Systemd 就是为了解决这些问题而诞生的。它的设计目标是,为系统的启动和管理提供一套
完整的解决方案。
@@ -51,11 +51,11 @@ simple, keep stupid"
(上图为 Systemd 架构图)
-## 系统管理
+## 3. 系统管理
Systemd 并不是一个命令,而是一组命令,涉及到系统管理的方方面面。
-### systemctl
+### 3.1. systemctl
`systemctl`是 Systemd 的主命令,用于管理系统。
@@ -82,7 +82,7 @@ $ sudo systemctl hybrid-sleep
$ sudo systemctl rescue
```
-### systemd-analyze
+### 3.2. systemd-analyze
`systemd-analyze`命令用于查看启动耗时。
@@ -100,7 +100,7 @@ $ systemd-analyze critical-chain
$ systemd-analyze critical-chain atd.service
```
-### hostnamectl
+### 3.3. hostnamectl
`hostnamectl`命令用于查看当前主机的信息。
@@ -112,7 +112,7 @@ $ hostnamectl
$ sudo hostnamectl set-hostname rhel7
```
-### localectl
+### 3.4. localectl
`localectl`命令用于查看本地化设置。
@@ -125,7 +125,7 @@ $ sudo localectl set-locale LANG=en_GB.utf8
$ sudo localectl set-keymap en_GB
```
-### timedatectl
+### 3.5. timedatectl
`timedatectl`命令用于查看当前时区设置。
@@ -142,7 +142,7 @@ $ sudo timedatectl set-time YYYY-MM-DD
$ sudo timedatectl set-time HH:MM:SS
```
-### loginctl
+### 3.6. loginctl
`loginctl`命令用于查看当前登录的用户。
@@ -157,9 +157,9 @@ $ loginctl list-users
$ loginctl show-user ruanyf
```
-## Unit
+## 4. Unit
-### 含义
+### 4.1. 含义
Systemd 可以管理所有系统资源。不同的资源统称为 Unit(单位)。
@@ -197,7 +197,7 @@ $ systemctl list-units --failed
$ systemctl list-units --type=service
```
-### Unit 的状态
+### 4.2. Unit 的状态
`systemctl status`命令用于查看系统状态和单个 Unit 的状态。
@@ -226,7 +226,7 @@ $ systemctl is-failed application.service
$ systemctl is-enabled application.service
```
-### Unit 管理
+### 4.3. Unit 管理
对于用户来说,最常用的是下面这些命令,用于启动和停止 Unit(主要是 service)。
@@ -259,7 +259,7 @@ $ systemctl show -p CPUShares httpd.service
$ sudo systemctl set-property httpd.service CPUShares=500
```
-### 依赖关系
+### 4.4. 依赖关系
Unit 之间存在依赖关系:A 依赖于 B,就意味着 Systemd 在启动 A 的时候,同时会去启
动 B。
@@ -277,9 +277,9 @@ $ systemctl list-dependencies nginx.service
$ systemctl list-dependencies --all nginx.service
```
-## Unit 的配置文件
+## 5. Unit 的配置文件
-### 概述
+### 5.1. 概述
每一个 Unit 都有一个配置文件,告诉 Systemd 怎么启动这个 Unit 。
@@ -306,7 +306,7 @@ $ sudo systemctl disable clamd@scan.service
配置文件的后缀名,就是该 Unit 的种类,比如`sshd.socket`。如果省略,Systemd 默认
后缀名为`.service`,所以`sshd`会被理解成`sshd.service`。
-### 配置文件的状态
+### 5.2. 配置文件的状态
`systemctl list-unit-files`命令用于列出所有配置文件。
@@ -351,7 +351,7 @@ $ sudo systemctl daemon-reload
$ sudo systemctl restart httpd.service
```
-### 配置文件的格式
+### 5.3. 配置文件的格式
配置文件就是普通的文本文件,可以用文本编辑器打开。
@@ -386,7 +386,7 @@ Directive2=value
注意,键值对的等号两侧不能有空格。
-### 配置文件的区块
+### 5.4. 配置文件的区块
`[Unit]`区块通常是配置文件的第一个区块,用来定义 Unit 的元数据,以及配置与其他
Unit 的关系。它的主要字段如下。
@@ -437,7 +437,7 @@ Unit 的关系。它的主要字段如下。
Unit 配置文件的完整字段清单,请参
考[官方文档](https://www.freedesktop.org/software/systemd/man/systemd.unit.html)。
-## Target
+## 6. Target
启动计算机的时候,需要启动大量的 Unit。如果每一次启动,都要一一写明本次启动需要
哪些 Unit,显然非常不方便。Systemd 的解决方案就是 Target。
@@ -497,7 +497,7 @@ Runlevel 6 | runlevel6.target -> reboot.target
配置文件存放在`/etc/sysconfig`目录。现在的配置文件主要存放在`/lib/systemd`目录
,在`/etc/systemd`目录里面的修改可以覆盖原始设置。
-## 日志管理
+## 7. 日志管理
Systemd 统一管理所有 Unit 的启动日志。带来的好处就是,可以只用`journalctl`一个命
令,查看所有日志(内核日志和应用日志)。日志的配置文件
@@ -588,16 +588,16 @@ $ sudo journalctl --vacuum-size=1G
$ sudo journalctl --vacuum-time=1years
```
-## 实战
+## 8. 实战
-### 开机启动
+### 8.1. 开机启动
对于那些支持 Systemd 的软件,安装的时候,会自动在`/usr/lib/systemd/system`目录添
加一个配置文件。
如果你想让该软件开机启动,就执行下面的命令(以`httpd.service`为例)。
-```
+```bash
$ sudo systemctl enable httpd
```
@@ -607,19 +607,19 @@ $ sudo systemctl enable httpd
这是因为开机时,`Systemd`只执行`/etc/systemd/system`目录里面的配置文件。这也意味
着,如果把修改后的配置文件放在该目录,就可以达到覆盖原始配置的效果。
-### 启动服务
+### 8.2. 启动服务
设置开机启动以后,软件并不会立即启动,必须等到下一次开机。如果想现在就运行该软件
,那么要执行`systemctl start`命令。
-```
+```bash
$ sudo systemctl start httpd
```
执行上面的命令以后,有可能启动失败,因此要用`systemctl status`命令查看一下该服务
的状态。
-```
+```bash
$ sudo systemctl status httpd
httpd.service - The Apache HTTP Server
@@ -649,28 +649,28 @@ CGroup: /system.slice/httpd.service
- `CGroup`块:应用的所有子进程
- 日志块:应用的日志
-### 停止服务
+### 8.3. 停止服务
终止正在运行的服务,需要执行`systemctl stop`命令。
-```
+```bash
$ sudo systemctl stop httpd.service
```
有时候,该命令可能没有响应,服务停不下来。这时候就不得不"杀进程"了,向正在运行的
进程发出`kill`信号。
-```
+```bash
$ sudo systemctl kill httpd.service
```
此外,重启服务要执行`systemctl restart`命令。
-```
+```bash
$ sudo systemctl restart httpd.service
```
-### 读懂配置文件
+### 8.4. 读懂配置文件
一个服务怎么启动,完全由它的配置文件决定。下面就来看,配置文件有些什么内容。
@@ -706,7 +706,7 @@ WantedBy=multi-user.target
下面依次解释每个区块的内容。
-### [Unit] 区块:启动顺序与依赖关系。
+### 8.5. [Unit] 区块:启动顺序与依赖关系。
`Unit`区块的`Description`字段给出当前服务的简单描述,`Documentation`字段给出文档
位置。
@@ -735,11 +735,11 @@ postgresql 之后启动,而没有定义依赖 postgresql 。上线后,由于
注意,`Wants`字段与`Requires`字段只涉及依赖关系,与启动顺序无关,默认情况下是同
时启动的。
-### [Service] 区块:启动行为
+### 8.6. [Service] 区块:启动行为
`Service`区块定义如何启动当前服务。
-#### 启动命令
+#### 8.6.1. 启动命令
许多软件都有自己的环境参数文件,该文件可以用`EnvironmentFile`字段读取。
@@ -787,19 +787,19 @@ post2
候,不影响其他命令的执行。比如,`EnvironmentFile=-/etc/sysconfig/sshd`(注意等号
后面的那个连词号),就表示即使`/etc/sysconfig/sshd`文件不存在,也不会抛出错误。
-#### 启动类型
+#### 8.6.2. 启动类型
`Type`字段定义启动类型。它可以设置的值如下。
- simple(默认值):`ExecStart`字段启动的进程为主进程
- forking:`ExecStart`字段将以`fork()`方式启动,此时父进程将会退出,子进程将成
-为主进程
+ 为主进程
- oneshot:类似于`simple`,但只执行一次,Systemd 会等它执行完,才启动其他服务
- dbus:类似于`simple`,但会等待 D-Bus 信号后启动
- notify:类似于`simple`,启动结束后会发出通知信号,然后 Systemd 再启动其他服
-务
+ 务
- idle:类似于`simple`,但是要等到其他任务都执行完,才会启动该服务。一种使用场
-合是为让该服务的输出,不与其他服务的输出相混合
+ 合是为让该服务的输出,不与其他服务的输出相混合
下面是一个`oneshot`的例子,笔记本电脑启动时,要把触摸板关掉,配置文件可以这样写
。
@@ -839,7 +839,7 @@ WantedBy=multi-user.target
行。这样的话,一旦使用`systemctl stop`命令停止服务,`ExecStop`指定的命令就会执行
,从而重新开启触摸板。
-#### 重启行为
+#### 8.6.3. 重启行为
`Service`区块有一些字段,定义了重启行为。
@@ -881,7 +881,7 @@ sshd 正常停止(比如执行`systemctl stop`命令),它就不会重启
> `RestartSec`字段:表示 Systemd 重启服务之前,需要等待的秒数。上面的例子设为等
> 待 42 秒。
-### [Install] 区块
+### 8.7. [Install] 区块
`Install`区块,定义如何安装这个配置文件,即怎样做到开机启动。
@@ -896,7 +896,7 @@ sshd 正常停止(比如执行`systemctl stop`命令),它就不会重启
Systemd 有默认的启动 Target。
-```
+```bash
$ systemctl get-default
multi-user.target
```
@@ -907,7 +907,7 @@ multi-user.target
使用 Target 的时候,`systemctl list-dependencies`命令和`systemctl isolate`命令也
很有用。
-```
+```bash
# 查看 multi-user.target 包含的所有服务
$ systemctl list-dependencies multi-user.target
@@ -921,11 +921,11 @@ $ sudo systemctl isolate shutdown.target
方文档有一张非常清晰的
[Target 依赖关系图](https://www.freedesktop.org/software/systemd/man/bootup.html#System%20Manager%20Bootup)。
-### Target 的配置文件
+### 8.8. Target 的配置文件
Target 也有自己的配置文件。
-```
+```bash
$ systemctl cat multi-user.target
[Unit]
@@ -948,11 +948,11 @@ AllowIsolate=yes
`rescue.target`之后启动,如果它们有启动的话。
- `AllowIsolate`:允许使用`systemctl isolate`命令切换到`multi-user.target`。
-### 修改配置文件后重启
+### 8.9. 修改配置文件后重启
修改配置文件以后,需要重新加载配置文件,然后重新启动相关服务。
-```
+```bash
# 重新加载配置文件
$ sudo systemctl daemon-reload
@@ -960,7 +960,7 @@ $ sudo systemctl daemon-reload
$ sudo systemctl restart foobar
```
-## 参考资料
+## 9. 参考资料
- [Systemd 入门教程:命令篇](http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2016/03/systemd-tutorial-commands.html)
- [Systemd 入门教程:实战篇](hhttp://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2016/03/systemd-tutorial-part-two.html)
diff --git a/docs/linux/ops/vim.md b/docs/linux/ops/vim.md
index 046fc47..3c8eae9 100644
--- a/docs/linux/ops/vim.md
+++ b/docs/linux/ops/vim.md
@@ -1,24 +1,4 @@
-# Vim 应用指南
-
-
-
-- [1. 概念](#1-概念)
- - [1.1. 什么是 vim](#11-什么是-vim)
- - [1.2. Vim 的模式](#12-vim-的模式)
-- [2. Vim 渐进学习](#2-vim-渐进学习)
- - [2.1. 存活](#21-存活)
- - [2.2. 感觉良好](#22-感觉良好)
- - [2.3. 更好,更强,更快](#23-更好更强更快)
- - [2.4. Vim 超能力](#24-vim-超能力)
-- [3. Vim Cheat Sheet](#3-vim-cheat-sheet)
- - [3.1. 经典版](#31-经典版)
- - [3.2. 入门版](#32-入门版)
- - [3.3. 进阶版](#33-进阶版)
- - [3.4. 增强版](#34-增强版)
- - [3.5. 文字版](#35-文字版)
-- [4. 资料](#4-资料)
-
-
+# Vim 应用
## 1. 概念
@@ -30,19 +10,19 @@ Vim 是从 vi 发展出来的一个文本编辑器。代码补完、编译及错
基本上 vi/vim 共分为三种模式,分别是**命令模式(Command mode)**,**插入模式(Insert mode)**和**底线命令模式(Last line mode)**。
-#### 命令模式
+#### 1.2.1. 命令模式
**用户刚刚启动 vi/vim,便进入了命令模式。**
此状态下敲击键盘动作会被 Vim 识别为命令,而非输入字符。
-#### 插入模式
+#### 1.2.2. 插入模式
**在命令模式下按下 `i` 就进入了输入模式。**
在输入模式下,你可以输入文本内容。
-#### 底线命令模式
+#### 1.2.3. 底线命令模式
**在命令模式下按下 `:`(英文冒号)就进入了底线命令模式。**
@@ -133,7 +113,7 @@ Vim 是从 vi 发展出来的一个文本编辑器。代码补完、编译及错
先恭喜你!你干的很不错。我们可以开始一些更为有趣的事了。在第三级,我们只谈那些和 vi 可以兼容的命令。
-#### 更好
+#### 2.3.1. 更好
下面,让我们看一下 vim 是怎么重复自己的:1515G
@@ -148,7 +128,7 @@ Vim 是从 vi 发展出来的一个文本编辑器。代码补完、编译及错
> - `.` → 重复上一个命令—— 100 “desu “.
> - `3.` → 重复 3 次 “desu” (注意:不是 300,你看,VIM 多聪明啊).
-#### 更强
+#### 2.3.2. 更强
你要让你的光标移动更有效率,你一定要了解下面的这些命令,**千万别跳过**。
@@ -167,7 +147,7 @@ Vim 是从 vi 发展出来的一个文本编辑器。代码补完、编译及错
>
> \> 如果你认为单词是由 blank 字符分隔符,那么你需要使用大写的 E 和 W。(注:程序语句)
>
-

+ >

下面,让我来说说最强的光标移动:
@@ -176,7 +156,7 @@ Vim 是从 vi 发展出来的一个文本编辑器。代码补完、编译及错
相信我,上面这三个命令对程序员来说是相当强大的。
-#### 更快
+#### 2.3.3. 更快
你一定要记住光标的移动,因为很多命令都可以和这些移动光标的命令连动。很多命令都可以如下来干:
@@ -206,7 +186,7 @@ Vim 是从 vi 发展出来的一个文本编辑器。代码补完、编译及错
你只需要掌握前面的命令,你就可以很舒服的使用 VIM 了。但是,现在,我们向你介绍的是 VIM 杀手级的功能。下面这些功能是我只用 vim 的原因。
-#### 在当前行上移动光标: `0` `^` `####`f`F`t`T`,``;`
+#### 2.4.1. 在当前行上移动光标: `0` `^` `####`f`F`t`T`,``;`
> - `0` → 到行头
> - `^` → 到本行的第一个非 blank 字符
@@ -216,11 +196,11 @@ Vim 是从 vi 发展出来的一个文本编辑器。代码补完、编译及错
> - `t,` → 到逗号前的第一个字符。逗号可以变成其它字符。
> - `3fa` → 在当前行查找第三个出现的 a。
> - `F` 和 `T` → 和 `f` 和 `t` 一样,只不过是相反方向。
-

+>

还有一个很有用的命令是 `dt"` → 删除所有的内容,直到遇到双引号—— `"。`
-#### 区域选择 `a
+
+
+
+
+
+





