I add English Translation of README.md |
||
|---|---|---|
| Day01-15 | ||
| Day16-20 | ||
| Day21-30 | ||
| Day31-35 | ||
| Day36-40 | ||
| Day41-55 | ||
| Day56-60 | ||
| Day61-65 | ||
| Day66-80 | ||
| Day81-90 | ||
| Day91-100 | ||
| res | ||
| 公开课 | ||
| 番外篇 | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| README.md | ||
| 更新日志.md | ||
README.md
Python - 100天从新手到大师
作者:骆昊
说明:从项目上线到获得8w+星标以来,一直收到反馈说基础部分(前15天的内容)对新手来说是比较困难的,建议有配套视频进行讲解。最近把基础部分的内容重新制作了一个名为“Python-Core-50-Courses”的项目,用更为简单通俗的方式重写了这部分内容并附带了视频讲解,初学者可以关注下这个新项目。国内用户如果访问GitHub比较慢的话,可以关注我的知乎号Python-Jack,上面的“从零开始学Python”专栏比较适合初学者,其他的专栏也在持续创作和更新中,欢迎大家关注并点赞评论。
需要加入QQ学习群的可以扫描下面的二维码,三个群加一个即可,不要重复进群。学习群会为大家提供学习资源和问题解答,如果有Python体验课和行业公开课会提前在群里通知大家,欢迎大家加入。

配套的视频在抖音和B站持续更新中,有兴趣的小伙伴可以关注我的抖音或B站账号,最近刚刚起号,还希望大家多多支持,非常感谢您!

Python应用领域和职业发展分析
简单的说,Python是一个“优雅”、“明确”、“简单”的编程语言。
- 学习曲线低,非专业人士也能上手
- 开源系统,拥有强大的生态圈
- 解释型语言,完美的平台可移植性
- 动态类型语言,支持面向对象和函数式编程
- 代码规范程度高,可读性强
Python在以下领域都有用武之地。
- 后端开发 - Python / Java / Go / PHP
- DevOps - Python / Shell / Ruby
- 数据采集 - Python / C++ / Java
- 量化交易 - Python / C++ / R
- 数据科学 - Python / R / Julia / Matlab
- 机器学习 - Python / R / C++ / Julia
- 自动化测试 - Python / Shell
作为一名Python开发者,根据个人的喜好和职业规划,可以选择的就业领域也非常多。
- Python后端开发工程师(服务器、云平台、数据接口)
- Python运维工程师(自动化运维、SRE、DevOps)
- Python数据分析师(数据分析、商业智能、数字化运营)
- Python数据挖掘工程师(机器学习、深度学习、算法专家)
- Python爬虫工程师
- Python测试工程师(自动化测试、测试开发)
说明:目前,数据分析和数据挖掘是非常热门的方向,因为不管是互联网行业还是传统行业都已经积累了大量的数据,各行各业都需要数据分析师从已有的数据中发现更多的商业价值,从而为企业的决策提供数据的支撑,这就是所谓的数据驱动决策。
给初学者的几个建议:
- Make English as your working language. (让英语成为你的工作语言)
- Practice makes perfect. (熟能生巧)
- All experience comes from mistakes. (所有的经验都源于你犯过的错误)
- Don't be one of the leeches. (不要当伸手党)
- Either outstanding or out. (要么出众,要么出局)
Day01~15 - Python语言基础
Day01 - 初识Python
- Python简介 - Python的历史 / Python的优缺点 / Python的应用领域
- 搭建编程环境 - Windows环境 / Linux环境 / MacOS环境
- 从终端运行Python程序 - Hello, world /
print函数 / 运行程序 - 使用IDLE - 交互式环境(REPL) / 编写多行代码 / 运行程序 / 退出IDLE
- 注释 - 注释的作用 / 单行注释 / 多行注释
Day02 - 语言元素
- 程序和进制 - 指令和程序 / 冯诺依曼机 / 二进制和十进制 / 八进制和十六进制
- 变量和类型 - 变量的命名 / 变量的使用 /
input函数 / 检查变量类型 / 类型转换 - 数字和字符串 - 整数 / 浮点数 / 复数 / 字符串 / 字符串基本操作 / 字符编码
- 运算符 - 数学运算符 / 赋值运算符 / 比较运算符 / 逻辑运算符 / 身份运算符 / 运算符的优先级
- 应用案例 - 华氏温度转换成摄氏温度 / 输入圆的半径计算周长和面积 / 输入年份判断是否是闰年
Day03 - 分支结构
- 分支结构的应用场景 - 条件 / 缩进 / 代码块 / 流程图
- if语句 - 简单的
if/if-else结构 /if-elif-else结构 / 嵌套的if - 应用案例 - 用户身份验证 / 英制单位与公制单位互换 / 掷骰子决定做什么 / 百分制成绩转等级制 / 分段函数求值 / 输入三条边的长度如果能构成三角形就计算周长和面积
Day04 - 循环结构
- 循环结构的应用场景 - 条件 / 缩进 / 代码块 / 流程图
- while循环 - 基本结构 /
break语句 /continue语句 - for循环 - 基本结构 /
range类型 / 循环中的分支结构 / 嵌套的循环 / 提前结束程序 - 应用案例 - 1~100求和 / 判断素数 / 猜数字游戏 / 打印九九表 / 打印三角形图案 / 猴子吃桃 / 百钱百鸡
Day05 - 构造程序逻辑
- 经典案例:水仙花数 / 百钱百鸡 / Craps赌博游戏
- 练习题目:斐波那契数列 / 完美数 / 素数
Day06 - 函数和模块的使用
- 函数的作用 - 代码的坏味道 / 用函数封装功能模块
- 定义函数 -
def关键字 / 函数名 / 参数列表 /return语句 / 调用自定义函数 - 调用函数 - Python内置函数 / 导入模块和函数
- 函数的参数 - 默认参数 / 可变参数 / 关键字参数 / 命名关键字参数
- 函数的返回值 - 没有返回值 / 返回单个值 / 返回多个值
- 作用域问题 - 局部作用域 / 嵌套作用域 / 全局作用域 / 内置作用域 / 和作用域相关的关键字
- 用模块管理函数 - 模块的概念 / 用自定义模块管理函数 / 命名冲突的时候会怎样(同一个模块和不同的模块)
Day07 - 字符串和常用数据结构
- 字符串的使用 - 计算长度 / 下标运算 / 切片 / 常用方法
- 列表基本用法 - 定义列表 / 用下表访问元素 / 下标越界 / 添加元素 / 删除元素 / 修改元素 / 切片 / 循环遍历
- 列表常用操作 - 连接 / 复制(复制元素和复制数组) / 长度 / 排序 / 倒转 / 查找
- 生成列表 - 使用
range创建数字列表 / 生成表达式 / 生成器 - 元组的使用 - 定义元组 / 使用元组中的值 / 修改元组变量 / 元组和列表转换
- 集合基本用法 - 集合和列表的区别 / 创建集合 / 添加元素 / 删除元素 / 清空
- 集合常用操作 - 交集 / 并集 / 差集 / 对称差 / 子集 / 超集
- 字典的基本用法 - 字典的特点 / 创建字典 / 添加元素 / 删除元素 / 取值 / 清空
- 字典常用操作 -
keys方法 /values方法 /items方法 /setdefault方法 - 基础练习 - 跑马灯效果 / 列表找最大元素 / 统计考试成绩的平均分 / Fibonacci数列 / 杨辉三角
- 综合案例 - 双色球选号 / 井字棋
Day08 - 面向对象编程基础
- 类和对象 - 什么是类 / 什么是对象 / 面向对象其他相关概念
- 定义类 - 基本结构 / 属性和方法 / 构造器 / 析构器 /
__str__方法 - 使用对象 - 创建对象 / 给对象发消息
- 面向对象的四大支柱 - 抽象 / 封装 / 继承 / 多态
- 基础练习 - 定义学生类 / 定义时钟类 / 定义图形类 / 定义汽车类
Day09 - 面向对象进阶
- 属性 - 类属性 / 实例属性 / 属性访问器 / 属性修改器 / 属性删除器 / 使用
__slots__ - 类中的方法 - 实例方法 / 类方法 / 静态方法
- 运算符重载 -
__add__/__sub__/__or__/__getitem__/__setitem__/__len__/__repr__/__gt__/__lt__/__le__/__ge__/__eq__/__ne__/__contains__ - 类(的对象)之间的关系 - 关联 / 继承 / 依赖
- 继承和多态 - 什么是继承 / 继承的语法 / 调用父类方法 / 方法重写 / 类型判定 / 多重继承 / 菱形继承(钻石继承)和C3算法
- 综合案例 - 工资结算系统 / 图书自动折扣系统 / 自定义分数类
Day10 - 图形用户界面和游戏开发
- 使用
tkinter开发GUI程序 - 使用
pygame三方库开发游戏应用 - “大球吃小球”游戏
Day11 - 文件和异常
- 读文件 - 读取整个文件 / 逐行读取 / 文件路径
- 写文件 - 覆盖写入 / 追加写入 / 文本文件 / 二进制文件
- 异常处理 - 异常机制的重要性 /
try-except代码块 /else代码块 /finally代码块 / 内置异常类型 / 异常栈 /raise语句 - 数据持久化 - CSV文件概述 /
csv模块的应用 / JSON数据格式 /json模块的应用
Day12 - 字符串和正则表达式
- 字符串高级操作 - 转义字符 / 原始字符串 / 多行字符串 /
in和not in运算符 /is_xxx方法 /join和split方法 /strip相关方法 /pyperclip模块 / 不变字符串和可变字符串 /StringIO的使用 - 正则表达式入门 - 正则表达式的作用 / 元字符 / 转义 / 量词 / 分组 / 零宽断言 /贪婪匹配与惰性匹配懒惰 / 使用
re模块实现正则表达式操作(匹配、搜索、替换、捕获) - 使用正则表达式 -
re模块 /compile函数 /group和groups方法 /match方法 /search方法 /findall和finditer方法 /sub和subn方法 /split方法 - 应用案例 - 使用正则表达式验证输入的字符串
Day13 - 进程和线程
- 进程和线程的概念 - 什么是进程 / 什么是线程 / 多线程的应用场景
- 使用进程 -
fork函数 /multiprocessing模块 / 进程池 / 进程间通信 - 使用线程 -
threading模块 /Thread类 /RLock类 /Condition类 / 线程池
Day14 - 网络编程入门和网络应用开发
- 计算机网络基础 - 计算机网络发展史 / “TCP-IP”模型 / IP地址 / 端口 / 协议 / 其他相关概念
- 网络应用模式 - “客户端-服务器”模式 / “浏览器-服务器”模式
- 基于HTTP协议访问网络资源 - 网络API概述 / 访问URL /
requests三方库 / 解析JSON格式数据 - Python网络编程 - 套接字的概念 /
socket模块 /socket函数 / 创建TCP服务器 / 创建TCP客户端 / 创建UDP服务器 / 创建UDP客户端 - 电子邮件 - SMTP协议 / POP3协议 / IMAP协议 /
smtplib模块 /poplib模块 /imaplib模块 - 短信服务 - 调用短信服务网关
Day15 - 图像和文档处理
- 用Pillow处理图片 - 图片读写 / 图片合成 / 几何变换 / 色彩转换 / 滤镜效果
- 读写Word文档 - 文本内容的处理 / 段落 / 页眉和页脚 / 样式的处理
- 读写Excel文件 -
xlrd/xlwt/openpyxl
Day16~Day20 - Python语言进阶
- 常用数据结构
- 函数的高级用法 - “一等公民” / 高阶函数 / Lambda函数 / 作用域和闭包 / 装饰器
- 面向对象高级知识 - “三大支柱” / 类与类之间的关系 / 垃圾回收 / 魔术属性和方法 / 混入 / 元类 / 面向对象设计原则 / GoF设计模式
- 迭代器和生成器 - 相关魔术方法 / 创建生成器的两种方式 /
- 并发和异步编程 - 多线程 / 多进程 / 异步IO /
async和await
Day21~30 - Web前端入门
- 用HTML标签承载页面内容
- 用CSS渲染页面
- 用JavaScript处理交互式行为
- jQuery入门和提高
- Vue.js入门
- Element的使用
- Bootstrap的使用
Day31~35 - 玩转Linux操作系统
- 操作系统发展史和Linux概述
- Linux基础命令
- Linux中的实用程序
- Linux的文件系统
- Vim编辑器的应用
- 环境变量和Shell编程
- 软件的安装和服务的配置
- 网络访问和管理
- 其他相关内容
Day36~40 - 数据库基础和进阶
- 关系型数据库概述
- MySQL的安装和使用
- SQL的使用
- DDL - 数据定义语言 -
create/drop/alter - DML - 数据操作语言 -
insert/delete/update - DQL - 数据查询语言 -
select - DCL - 数据控制语言 -
grant/revoke - MySQL新特性
- 窗口函数的应用
- JSON数据类型
- 相关知识
- 数据完整性和一致性
- 视图、函数、过程、触发器
- 事务和锁
- 执行计划和索引
- 范式理论和反范式设计
- 在Python中操作MySQL
Day41~55 - 实战Django
Day41 - Django快速上手
- Web应用工作机制
- HTTP请求和响应
- Django框架概述
- 5分钟快速上手
Day42 - 深入模型
- 关系型数据库配置
- 使用ORM完成对模型的CRUD操作
- 管理后台的使用
- Django模型最佳实践
- 模型定义参考
Day43 - 静态资源和Ajax请求
- 加载静态资源
- Ajax概述
- 用Ajax实现投票功能
Day44 - Cookie和Session
- 实现用户跟踪
- cookie和session的关系
- Django框架对session的支持
- 视图函数中的cookie读写操作
Day45 - 报表和日志
- 通过
HttpResponse修改响应头 - 使用
StreamingHttpResponse处理大文件 - 使用
xlwt生成Excel报表 - 使用
reportlab生成PDF报表 - 使用ECharts生成前端图表
Day46 - 日志和调试工具栏
- 配置日志
- 配置Django-Debug-Toolbar
- 优化ORM代码
Day47 - 中间件的应用
- 什么是中间件
- Django框架内置的中间件
- 自定义中间件及其应用场景
Day48 - 前后端分离开发入门
- 返回JSON格式的数据
- 用Vue.js渲染页面
Day49 - RESTful架构和DRF入门
Day50 - RESTful架构和DRF进阶
Day51 - 使用缓存
-
网站优化第一定律
-
在Django项目中使用Redis提供缓存服务
-
在视图函数中读写缓存
-
使用装饰器实现页面缓存
-
为数据接口提供缓存服务
Day52 - 接入三方平台
- 文件上传表单控件和图片文件预览
- 服务器端如何处理上传的文件
Day53 - 异步任务和定时任务
- 网站优化第二定律
- 配置消息队列服务
- 在项目中使用Celery实现任务异步化
- 在项目中使用Celery实现定时任务
Day54 - 单元测试
Day55 - 项目上线
- Python中的单元测试
- Django框架对单元测试的支持
- 使用版本控制系统
- 配置和使用uWSGI
- 动静分离和Nginx配置
- 配置HTTPS
- 配置域名解析
Day56~60 - 用FastAPI开发数据接口
- FastAPI五分钟上手
- 请求和响应
- 接入关系型数据库
- 依赖注入
- 中间件
- 异步化
- 虚拟化部署(Docker)
- 项目实战:车辆违章查询项目
Day61~65 - 爬虫开发
Day61 - 网络数据采集概述
- 网络爬虫的概念及其应用领域
- 网络爬虫的合法性探讨
- 开发网络爬虫的相关工具
- 一个爬虫程序的构成
Day62 - 数据抓取和解析
- 使用
requests三方库实现数据抓取 - 页面解析的三种方式
- 正则表达式解析
- XPath解析
- CSS选择器解析
Day63 - Python中的并发编程
Day64 - 使用Selenium抓取网页动态内容
Day65 - 爬虫框架Scrapy简介
Day66~80 - 数据分析
Day66 - 数据分析概述
Day67 - 环境准备
Day68 - NumPy的应用-1
Day69 - NumPy的应用-2
Day70 - NumPy的应用-3
Day71 - NumPy的应用-4
Day72 - 深入浅出pandas-1
Day73 - 深入浅出pandas-2
Day74 - 深入浅出pandas-3
Day75 - 深入浅出pandas-4
Day76 - 深入浅出pandas-5
Day77 - 深入浅出pandas-6
Day78 - 数据可视化-1
Day79 - 数据可视化-2
Day80 - 数据可视化-3
Day81~90 - 机器学习和深度学习
Day81 - 机器学习基础
Day82 - k最近邻分类
Day83 - 决策树
Day84 - 贝叶斯分类
Day85 - 支持向量机
Day86 - K-均值聚类
Day87 - 回归分析
Day88 - 深度学习入门
Day89 - PyTorch概述
Day90 - PyTorch实战
Day91~100 - 团队项目开发
第91天:团队项目开发的问题和解决方案
-
软件过程模型
-
经典过程模型(瀑布模型)
- 可行性分析(研究做还是不做),输出《可行性分析报告》。
- 需求分析(研究做什么),输出《需求规格说明书》和产品界面原型图。
- 概要设计和详细设计,输出概念模型图(ER图)、物理模型图、类图、时序图等。
- 编码 / 测试。
- 上线 / 维护。
瀑布模型最大的缺点是无法拥抱需求变化,整套流程结束后才能看到产品,团队士气低落。
-
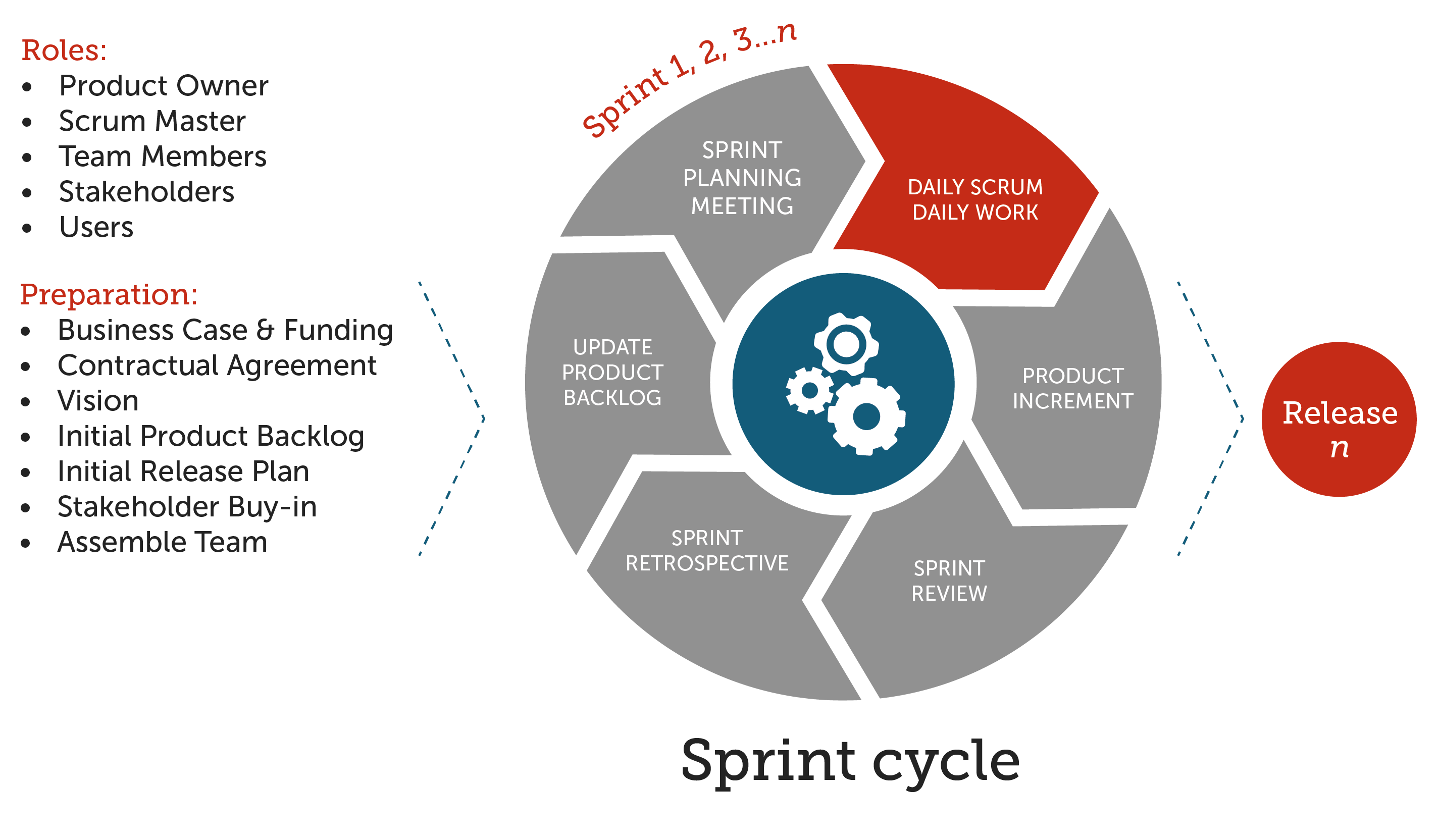
敏捷开发(Scrum)- 产品所有者、Scrum Master、研发人员 - Sprint
- 产品的Backlog(用户故事、产品原型)。
- 计划会议(评估和预算)。
- 日常开发(站立会议、番茄工作法、结对编程、测试先行、代码重构……)。
- 修复bug(问题描述、重现步骤、测试人员、被指派人)。
- 发布版本。
- 评审会议(Showcase,用户需要参与)。
- 回顾会议(对当前迭代周期做一个总结)。
补充:敏捷软件开发宣言
- 个体和互动 高于 流程和工具
- 工作的软件 高于 详尽的文档
- 客户合作 高于 合同谈判
- 响应变化 高于 遵循计划
角色:产品所有者(决定做什么,能对需求拍板的人)、团队负责人(解决各种问题,专注如何更好的工作,屏蔽外部对开发团队的影响)、开发团队(项目执行人员,具体指开发人员和测试人员)。
准备工作:商业案例和资金、合同、憧憬、初始产品需求、初始发布计划、入股、组建团队。
敏捷团队通常人数为8-10人。
工作量估算:将开发任务量化,包括原型、Logo设计、UI设计、前端开发等,尽量把每个工作分解到最小任务量,最小任务量标准为工作时间不能超过两天,然后估算总体项目时间。把每个任务都贴在看板上面,看板上分三部分:to do(待完成)、in progress(进行中)和done(已完成)。
-
-
项目团队组建
-
团队的构成和角色
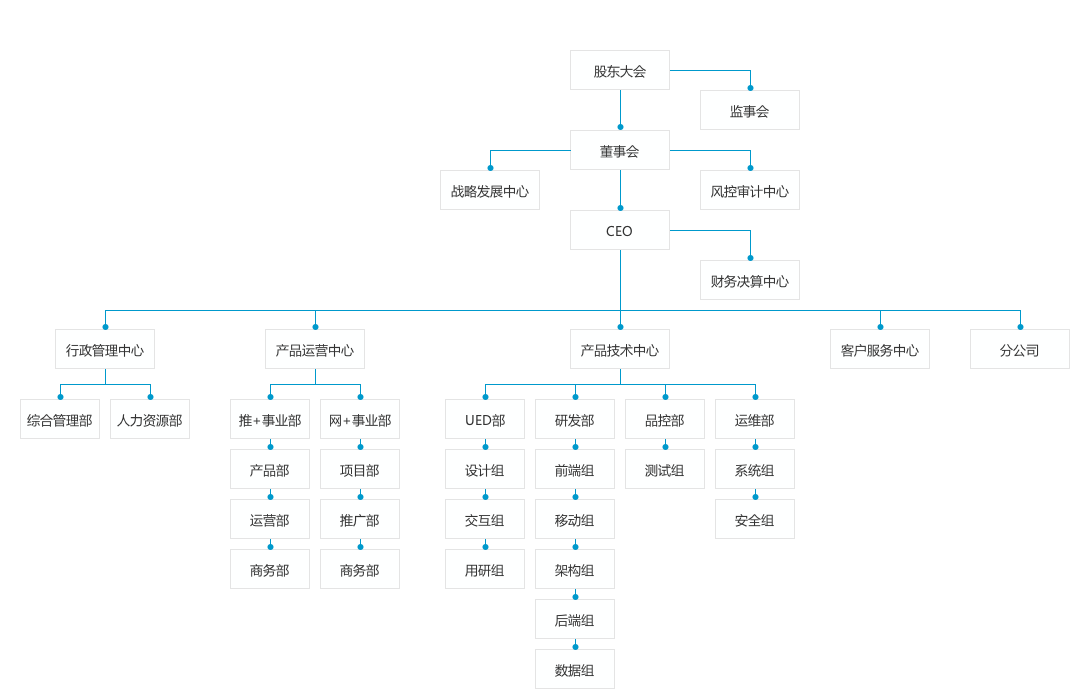
说明:谢谢付祥英女士帮助我绘制了下面这张精美的公司组织架构图。
-
编程规范和代码审查(
flake8、pylint) -
Python中的一些“惯例”(请参考《Python惯例-如何编写Pythonic的代码》)
-
影响代码可读性的原因:
- 代码注释太少或者没有注释
- 代码破坏了语言的最佳实践
- 反模式编程(意大利面代码、复制-黏贴编程、自负编程、……)
-
-
团队开发工具介绍
请参考《团队项目开发的问题和解决方案》。
项目选题和理解业务
-
选题范围设定
-
CMS(用户端):新闻聚合网站、问答/分享社区、影评/书评网站等。
-
MIS(用户端+管理端):KMS、KPI考核系统、HRS、CRM系统、供应链系统、仓储管理系统等。
-
App后台(管理端+数据接口):二手交易类、报刊杂志类、小众电商类、新闻资讯类、旅游类、社交类、阅读类等。
-
其他类型:自身行业背景和工作经验、业务容易理解和把控。
-
-
需求理解、模块划分和任务分配
- 需求理解:头脑风暴和竞品分析。
- 模块划分:画思维导图(XMind),每个模块是一个枝节点,每个具体的功能是一个叶节点(用动词表述),需要确保每个叶节点无法再生出新节点,确定每个叶子节点的重要性、优先级和工作量。
- 任务分配:由项目负责人根据上面的指标为每个团队成员分配任务。
-
制定项目进度表(每日更新)
模块 功能 人员 状态 完成 工时 计划开始 实际开始 计划结束 实际结束 备注 评论 添加评论 王大锤 正在进行 50% 4 2018/8/7 2018/8/7 删除评论 王大锤 等待 0% 2 2018/8/7 2018/8/7 查看评论 白元芳 正在进行 20% 4 2018/8/7 2018/8/7 需要进行代码审查 评论投票 白元芳 等待 0% 4 2018/8/8 2018/8/8 -
OOAD和数据库设计
-
UML(统一建模语言)的类图
-
通过模型创建表(正向工程),例如在Django项目中可以通过下面的命令创建二维表。
python manage.py makemigrations app python manage.py migrate -
使用PowerDesigner绘制物理模型图。
-
通过数据表创建模型(反向工程),例如在Django项目中可以通过下面的命令生成模型。
python manage.py inspectdb > app/models.py
第92天:Docker容器详解
- Docker简介
- 安装Docker
- 使用Docker创建容器(Nginx、MySQL、Redis、Gitlab、Jenkins)
- 构建Docker镜像(Dockerfile的编写和相关指令)
- 容器编排(Docker-compose)
- 集群管理(Kubernetes)
第93天:MySQL性能优化
第94天:网络API接口设计
第95天:[使用Django开发商业项目](./Day91-100/95.使用Django开发商业项 目.md)
项目开发中的公共问题
- 数据库的配置(多数据库、主从复制、数据库路由)
- 缓存的配置(分区缓存、键设置、超时设置、主从复制、故障恢复(哨兵))
- 日志的配置
- 分析和调试(Django-Debug-ToolBar)
- 好用的Python模块(日期计算、图像处理、数据加密、三方API)
REST API设计
- RESTful架构
- API接口文档的撰写
- django-REST-framework的应用
项目中的重点难点剖析
- 使用缓存缓解数据库压力 - Redis
- 使用消息队列做解耦合和削峰 - Celery + RabbitMQ
第96天:软件测试和自动化测试
单元测试
- 测试的种类
- 编写单元测试(
unittest、pytest、nose2、tox、ddt、……) - 测试覆盖率(
coverage)
Django项目部署
- 部署前的准备工作
- 关键设置(SECRET_KEY / DEBUG / ALLOWED_HOSTS / 缓存 / 数据库)
- HTTPS / CSRF_COOKIE_SECUR / SESSION_COOKIE_SECURE
- 日志相关配置
- Linux常用命令回顾
- Linux常用服务的安装和配置
- uWSGI/Gunicorn和Nginx的使用
- Gunicorn和uWSGI的比较
- 对于不需要大量定制化的简单应用程序,Gunicorn是一个不错的选择,uWSGI的学习曲线比Gunicorn要陡峭得多,Gunicorn的默认参数就已经能够适应大多数应用程序。
- uWSGI支持异构部署。
- 由于Nginx本身支持uWSGI,在线上一般都将Nginx和uWSGI捆绑在一起部署,而且uWSGI属于功能齐全且高度定制的WSGI中间件。
- 在性能上,Gunicorn和uWSGI其实表现相当。
- Gunicorn和uWSGI的比较
- 使用虚拟化技术(Docker)部署测试环境和生产环境
性能测试
- AB的使用
- SQLslap的使用
- sysbench的使用
自动化测试
- 使用Shell和Python进行自动化测试
- 使用Selenium实现自动化测试
- Selenium IDE
- Selenium WebDriver
- Selenium Remote Control
- 测试工具Robot Framework介绍
第97天:电商网站技术要点剖析
第98天:项目部署上线和性能调优
- MySQL数据库调优
- Web服务器性能优化
- Nginx负载均衡配置
- Keepalived实现高可用
- 代码性能调优
- 多线程
- 异步化
- 静态资源访问优化
- 云存储
- CDN
第99天:面试中的公共问题
第100天:Python面试题实录
Python - From Novice to Master in 100 Days
Author: Luo Hao
Note: From the launch of the project to the acquisition of 8w+ stars, we have received feedback that the basic part (the content of the first 15 days) is difficult for novices, and it is recommended to have supporting videos to explain it. Recently, the basic part of the content was remade into a project called "Python-Core-50-Courses", ** use This part of the content has been rewritten in a simpler and more popular way and comes with video explanation**. Beginners can pay attention to this new project. If domestic users are slow to access GitHub, they can follow my Zhihu account Python-Jack, the above "Learn Python from scratch" " column is more suitable for beginners. Other columns are also being continuously created and updated. Everyone is welcome to follow, like and comment.
If you want to join the QQ learning group, you can scan the QR code below. Just add one of the three groups. Do not join the group repeatedly. The study group will provide you with learning resources and question answers. If there are Python experience classes and industry open classes, you will be notified in the group in advance. Everyone is welcome to join.

The supporting videos are being continuously updated on Douyin and Bilibili. Interested friends can follow my Douyin or Bilibili account. I have just opened my account recently. I hope you can support me a lot. Thank you very much!

Python application fields and career development analysis
Simply put, Python is an "elegant", "clear" and "simple" programming language.
-Low learning curve, even non-professionals can get started
- Open source system with a strong ecosystem
- Interpreted language, perfect platform portability
- Dynamically typed language, supporting object-oriented and functional programming
- The code is highly standardized and readable
Python is useful in the following fields.
- Backend Development - Python/Java/Go/PHP
- DevOps - Python/Shell/Ruby
- Data Acquisition - Python/C++/Java
- Quantitative Trading - Python/C++/R
- Data Science - Python/R/Julia/Matlab
- Machine Learning - Python/R/C++/Julia
- Automated testing - Python/Shell
As a Python developer, there are many employment fields to choose from based on personal preferences and career plans.
- Python back-end development engineer (server, cloud platform, data interface)
- Python operation and maintenance engineer (automated operation and maintenance, SRE, DevOps)
- Python data analyst (data analysis, business intelligence, digital operations)
- Python data mining engineer (machine learning, deep learning, algorithm expert)
- Python crawler engineer
- Python test engineer (automated testing, test development)
-
Note: Currently, data analysis and data mining are very popular directions, because both the Internet industry and traditional industries have accumulated a large amount of data, and all walks of life need data analysts from the past. More business value is found in some data, thereby providing data support for corporate decision-making. This is the so-called data-driven decision-making.
A few suggestions for beginners:
- Make English as your working language.
- Practice makes perfect.
- All experience comes from mistakes.
- Don't be one of the leeches.
- Either outstanding or out. (either outstanding or out)
Day01~15 - Python Language Basics
Day01 - [First introduction to Python](./Day01-15/01. First introduction to Python.md)
- Introduction to Python - History of Python / Advantages and disadvantages of Python / Application fields of Python
- Build a programming environment - Windows environment / Linux environment / MacOS environment
- Run Python program from terminal - Hello, world /
printfunction / Run program - Using IDLE - Interactive environment (REPL) / Write multiple lines of code / Run program / Exit IDLE
- Comments - The role of comments / single line comments / multi-line comments
Day02 - [Language Element](./Day01-15/02.Language Element.md)
- Programs and bases - Instructions and programs / Von Neumann machine / Binary and decimal / Octal and hexadecimal
- Variables and types - Naming of variables / Usage of variables /
inputfunction / Checking variable types / Type conversion - Numbers and strings - Integers/Floating point numbers/Complex numbers/Strings/Basic string operations/Character encoding
- Operators - Mathematical operators / Assignment operators / Comparison operators / Logical operators / Identity operators / Priority of operators
- Application case - Convert Fahrenheit temperature to Celsius temperature / Enter the radius of the circle to calculate the circumference and area / Enter the year to determine whether it is a leap year
Day03 - [Branch Structure](./Day01-15/03.Branch Structure.md)
- Application scenarios of branch structures - Conditions/indentation/code blocks/flow charts
- if statement - simple
if/if-elsestructure /if-elif-elsestructure / nestedif - Application cases - User authentication / Interchange of imperial units and metric units / Rolling dice to decide what to do / Converting percentile scores to grades / Evaluating piecewise functions / Entering the lengths of three sides and calculating the perimeter and area if a triangle can be formed
Day04 - [Loop Structure](./Day01-15/04.Loop Structure.md)
- Application scenarios of loop structures - Conditions/indentation/code blocks/flow charts
- while loop - basic structure /
breakstatement /continuestatement - for loop - basic structure /
rangetype / branch structure in the loop / nested loop / early end of the program - Application cases - Summing 1~100 / Determining prime numbers / Guessing number games / Printing ninety-nine tables / Printing triangle patterns / Monkey eating peaches / Hundreds of coins and hundreds of chickens
Day05 - [Construct program logic](./Day01-15/05. Construct program logic.md)
- Classic cases: Number of Daffodils / Hundred Money and Hundred Chickens / Craps Gambling Game
- Practice questions: Fibonacci Sequence/Perfect Numbers/Prime Numbers
Day06 - [Use of functions and modules](./Day01-15/06.Use of functions and modules.md)
- The role of functions - Bad smell of code / Use functions to encapsulate functional modules
- Define function -
defkeyword / function name / parameter list /returnstatement / call custom function - Call functions - Python built-in functions/Import modules and functions
- Parameters of functions - Default parameters / variable parameters / keyword parameters / named keyword parameters
- The return value of the function - no return value / return a single value / return multiple values
- Scope issues - local scope / nested scope / global scope / built-in scope / keywords related to scope
- Using module management functions - The concept of modules / Using custom module management functions / What happens when there is a naming conflict (the same module and different modules)
Day07 - [Strings and Common Data Structures](./Day01-15/07.Strings and Common Data Structures.md)
- Use of strings - Calculating length/subscript operation/slicing/common methods
- Basic usage of lists - Define lists / use the following table to access elements / subscript out of bounds / add elements / delete elements / modify elements / slice / loop traversal
- Common operations on lists - connection / copy (copy elements and copy arrays) / length / sort / reverse / search
- Generate lists - use
rangeto create lists of numbers / generate expressions / generators - Use of tuples - Define tuples/Use values in tuples/Modify tuple variables/Tuple and list conversions
- Basic usage of sets - The difference between sets and lists / Create a set / Add elements / Delete elements / Clear
- Common operations on sets - intersection/union/difference/symmetric difference/subset/superset
- Basic usage of dictionary - Features of dictionary / Create dictionary / Add element / Delete element / Get value / Clear
- Common dictionary operations -
keysmethod /valuesmethod /itemsmethod /setdefaultmethod - Basic exercises - Marquee effect / Find the largest element in a list / Average score of statistical test scores / Fibonacci sequence / Yang Hui triangle
- Comprehensive Cases - Double Color Ball Number Selection/Tic-Tac-Toe
Day08 - [Basics of Object-Oriented Programming](./Day01-15/08.Basics of Object-Oriented Programming.md)
- Classes and objects - What is a class / What is an object / Other related concepts of object-oriented
- Define class - Basic structure / Attributes and methods / Constructor / Destructor /
__str__method - Use objects - Create objects/Send messages to objects
- The four pillars of object-oriented - abstraction/encapsulation/inheritance/polymorphism
- Basic exercises - Define student class / Define clock class / Define graphics class / Define car class
Day09 - [Advanced Object-Oriented](./Day01-15/09.Advanced Object-Oriented.md)
- Attributes - class attributes / instance attributes / attribute accessors / attribute modifiers / attribute deleters / use
__slots__ - Methods in classes - Instance methods/class methods/static methods
- Operator overloading -
__add__/__sub__/__or__/__getitem__/__setitem__/__len__/__repr__/__gt__/__lt__/__le__/__ge__/__eq__/__ne__/__contains__ - Relationship between classes (objects) - Association/Inheritance/Dependence
- Inheritance and polymorphism - What is inheritance / Syntax of inheritance / Calling parent class methods / Method overriding / Type determination / Multiple inheritance / Diamond inheritance (diamond inheritance) and C3 algorithm
- Comprehensive cases - Salary settlement system / Automatic book discount system / Customized score categories
Day10 - [Graphical User Interface and Game Development](./Day01-15/10.Graphical User Interface and Game Development.md)
- Use
tkinterto develop GUI programs - Use
pygamethird-party library to develop game applications - "Big ball eats small ball" game
Day11 - [Files and Exceptions](./Day01-15/11.Files and Exceptions.md)
- Read file - read the entire file / read line by line / file path
- Write file - Overwrite/Append/Text file/Binary file
- Exception handling - The importance of exception mechanism /
try-exceptcode block /elsecode block /finallycode block / Built-in exception types / Exception stack /raisestatement - Data persistence - CSV file overview / Application of
csvmodule / JSON data format / Application ofjsonmodule
Day12 - [Strings and Regular Expressions](./Day01-15/12.Strings and Regular Expressions.md)
- Advanced operations on strings - Escape characters/original strings/multiline strings/
inandnot inoperators/is_xxxmethods/joinandsplitmethods/striprelated methods/pyperclipmodule/immutable strings and variable strings/use ofStringIO - Introduction to regular expressions - The role of regular expressions/metacharacters/escaping/quantifiers/grouping/zero-width assertions/greedy matching and lazy matching lazy/use the
remodule to implement regular expression operations (matching, searching, replacing, capture) - Using regular expressions -
remodule /compilefunction /groupandgroupsmethods /matchmethod /searchmethod /findallandfinditermethods /subandsubnmethod/splitmethod - Application case - Use regular expressions to validate input strings
Day13 - [Processes and Threads](./Day01-15/13.Processes and Threads.md)
- Concepts of processes and threads - What is a process / What is a thread / Multi-threading application scenarios
- Using processes -
forkfunction /multiprocessingmodule / process pool / inter-process communication - Using threads -
threadingmodule /Threadclass /RLockclass /Conditionclass / thread pool
Day14 - [Introduction to Network Programming and Network Application Development](./Day01-15/14.Introduction to Network Programming and Network Application Development.md)
- Basics of computer network - History of computer network development / "TCP-IP" model / IP address / port / protocol / other related concepts
- Network application mode - "Client-Server" mode / "Browser-Server" mode
- Access network resources based on HTTP protocol - Network API overview / Access URL /
requeststhird-party library / Parse JSON format data - Python network programming - The concept of sockets /
socketmodule /socketfunction / Create TCP server / Create TCP client / Create UDP server / Create UDP client - Email - SMTP protocol / POP3 protocol / IMAP protocol /
smtplibmodule /poplibmodule /imaplibmodule - SMS service - Call SMS service gateway
Day15 - [Image and Document Processing](./Day01-15/15.Image and Office Document Processing.md)
- Use Pillow to process pictures - picture reading and writing / picture synthesis / geometric transformation / color conversion / filter effects
- Read and write Word documents - Processing of text content/paragraphs/headers and footers/style processing
- Read and write Excel files -
xlrd/xlwt/openpyxl
Day16~Day20 - [Python Language Advanced](./Day16-20/16-20.Python Language Advanced.md)
- Common data structures
- Advanced usage of functions - "First-class citizens" / Higher-order functions / Lambda functions / Scope and closure / Decorators
- Advanced knowledge of object-oriented - "Three Pillars" / Relationship between classes / Garbage collection / Magic properties and methods / Mixing / Metaclass / Object-oriented design principles / GoF design pattern
- Iterators and generators - Related magic methods / Two ways to create a generator /
- Concurrent and asynchronous programming - multi-threading / multi-process / asynchronous IO /
asyncandawait
Day21~30 - [Introduction to Web front-end](./Day21-30/21-30.Web front-end overview.md)
- Use HTML tags to carry page content
- Render the page with CSS
- Handle interactive behavior with JavaScript
- Getting started with jQuery and improving it
- Getting started with Vue.js -Use of Element -Usage of Bootstrap
Day31~35 - [Fun with the Linux operating system](./Day31-35/31-35.Fun with the Linux operating system.md)
- History of operating system development and overview of Linux
- Linux basic commands
- Utilities in Linux
- Linux file system
- Application of Vim editor
- Environment variables and shell programming
- Software installation and service configuration
- Network access and management
- Other related content
Day36~40 - Database Basics and Advanced
- Overview of relational databases
- Installation and use of MySQL
- Use of SQL
- DDL - Data Definition Language -
create/drop/alter - DML - Data manipulation language -
insert/delete/update - DQL - Data Query Language -
select - DCL - Data Control Language -
grant/revoke - MySQL new features
- Application of window functions
- JSON data type
- related information
- Data integrity and consistency
- Views, functions, procedures, triggers
- Transactions and locks
- Execution plan and index
- Paradigm theory and anti-paradigm design
- Operate MySQL in Python
Day41~55 - Practical Django
Day41 - [Django Quick Start](./Day41-55/41.Django Quick Start.md)
- Web application working mechanism
- HTTP requests and responses
- Django framework overview
- Get started quickly in 5 minutes
Day42 - [In-depth model](./Day41-55/42.In-depth model.md)
- Relational database configuration
- Use ORM to complete CRUD operations on the model
- Use of management backend
- Django model best practices
- Model definition reference
Day43 - [Static Resources and Ajax Requests](./Day41-55/43.Static Resources and Ajax Requests.md)
- Load static resources
- Ajax Overview
- Use Ajax to implement voting function
Day44 - [Cookie and Session](./Day41-55/44.Cookie and Session.md)
- Implement user tracking -The relationship between cookie and session
- Django framework’s support for sessions
- Cookie reading and writing operations in view functions
Day45 - [Reports and Logs](./Day41-55/45.Create Reports.md)
- Modify response headers through
HttpResponse - Use
StreamingHttpResponseto handle large files - Use
xlwtto generate Excel reports - Use
reportlabto generate PDF reports - Use ECharts to generate front-end charts
Day46 - [Log and Debug Toolbar](./Day41-55/46.Log and Debug Toolbar.md)
- Configuration log
- Configure Django-Debug-Toolbar
- Optimize ORM code
Day47 - [Application of middleware](./Day41-55/47.Application of middleware.md)
- What is middleware -Middleware built into the Django framework
- Custom middleware and its application scenarios
Day48 - [Introduction to front-end and back-end separation development](./Day41-55/48. Introduction to front-end and front-end separation development.md)
- Return data in JSON format
- Render the page with Vue.js
Day49 - [Getting Started with RESTful Architecture and DRF](./Day41-55/49.Getting Started with RESTful Architecture and DRF.md)
Day50 - [RESTful Architecture and DRF Advanced](./Day41-55/50.RESTful Architecture and DRF Advanced.md)
Day51 - [Use cache](./Day41-55/51.Use cache.md)
-
The first law of website optimization
-
Use Redis to provide caching services in Django projects
-
Read and write cache in view functions
-
Use decorators to implement page caching
-
Provide caching services for data interfaces
Day52 - [Access to the third-party platform](./Day41-55/52.Access to the third-party platform.md)
- File upload form control and image file preview
- How the server handles uploaded files
Day53 - [Asynchronous tasks and scheduled tasks](./Day41-55/53.Asynchronous tasks and scheduled tasks.md)
- The second law of website optimization
- Configure message queue service
- Use Celery to implement task asynchronousization in the project
- Use Celery to implement scheduled tasks in the project
Day54 - [Unit Test](./Day41-55/54.Unit Test.md)
Day55 - [Project online](./Day41-55/55.Project online.md)
- Unit testing in Python
- Django framework support for unit testing
- Use version control system
- Configure and use uWSGI
- Static and dynamic separation and Nginx configuration
- Configure HTTPS
- Configure domain name resolution
Day56~60 - [Develop data interface using FastAPI](./Day56-60/56-60.Develop data interface using FastAPI.md)
- Get started with FastAPI in five minutes
- Requests and responses
- Access to relational database
- Dependency injection
- middleware
- Asynchronous
- Virtualization deployment (Docker)
- Project practice: vehicle violation inquiry project
Day61~65 - Reptile Development
Day61 - [Overview of Network Data Collection](./Day61-65/61.Overview of Network Data Collection.md)
- The concept of web crawler and its application fields
- Discussion on the legality of web crawlers
- Related tools for developing web crawlers
- The composition of a crawler program
Day62 - Data capture and parsing
- [Use
requeststhird-party library to implement data capture](./Day61-65/62. Use Python to obtain network resources-1.md) - [Three ways of page parsing](./Day61-65/62. Parsing HTML pages with Python-2.md)
- Regular expression parsing
- XPath parsing
- CSS selector parsing
Day63 - Concurrent Programming in Python
- [Multi-threading](./Day61-65/63.Concurrent Programming in Python-1.md)
- [Multiple processes](./Day61-65/63.Concurrent programming in Python-2.md)
- [Asynchronous I/O](./Day61-65/63.Concurrent Programming in Python-3.md)
Day64 - [Use Selenium to crawl dynamic content of web pages](./Day61-65/64.Use Selenium to crawl dynamic content of web pages.md)
Day65 - [Introduction to crawler framework Scrapy](./Day61-65/65.Introduction to crawler framework Scrapy.md)
Day66~80 - Data Analysis
Day66 - [Data Analysis Overview](./Day66-80/66.Data Analysis Overview.md)
Day67 - [Environment Preparation](./Day66-80/67.Environment Preparation.md)
Day68 - [Application of NumPy-1](./Day66-80/68.Application of NumPy-1.md)
Day69 - [Application of NumPy-2](./Day66-80/69.Application of NumPy-2.md)
Day70 - [Application of NumPy-3](./Day66-80/70.Application of NumPy-3.md)
Day71 - [Application of NumPy-4](./Day66-80/71.Application of NumPy-4.md)
Day72 - [In-depth explanation of pandas-1](./Day66-80/72. In-depth explanation of pandas-1.md)
Day73 - [Introduction to pandas-2](./Day66-80/73.In-depth explanation of pandas-2.md)
Day74 - [In-depth explanation of pandas-3](./Day66-80/74. In-depth explanation of pandas-3.md)
Day75 - [Introduction to pandas-4](./Day66-80/75.In-depth explanation of pandas-4.md)
Day76 - [In-depth explanation of pandas-5](./Day66-80/76. In-depth explanation of pandas-5.md)
Day77 - [In-depth explanation of pandas-6](./Day66-80/77. In-depth explanation of pandas-6.md)
Day78 - [Data Visualization-1](./Day66-80/78.Data Visualization-1.md)
Day79 - [Data Visualization-2](./Day66-80/79.Data Visualization-2.md)
Day80 - [Data Visualization-3](./Day66-80/80.Data Visualization-3.md)
Day81~90 - Machine Learning and Deep Learning
Day81 - [Basics of Machine Learning](./Day81-90/81.Basics of Machine Learning.md)
Day82 - [k nearest neighbor classification](./Day81-90/82.k nearest neighbor classification.md)
Day83 - [Decision Tree](./Day81-90/83.Decision Tree.md)
Day84 - [Bayesian Classification](./Day81-90/84.Bayesian Classification.md)
Day85 - [Support Vector Machine](./Day81-90/85.Support Vector Machine.md)
Day86 - [K-means clustering](./Day81-90/86.K-means clustering.md)
Day87 - [Regression Analysis](./Day81-90/87.Regression Analysis.md)
Day88 - [Introduction to Deep Learning](./Day81-90/88.Introduction to Deep Learning.md)
Day89 - [PyTorch Overview](./Day81-90/89.PyTorch Overview.md)
Day90 - [PyTorch in action](./Day81-90/90.PyTorch in action.md)
Day91~100 - Team Project Development
Day 91: [Problems and Solutions for Team Project Development](./Day91-100/91.Problems and Solutions for Team Project Development.md)
-
Software process model
-
Classic process model (waterfall model)
- Feasibility analysis (whether to do the research or not), and output the "Feasibility Analysis Report".
- Requirements analysis (research on what to do), output "Requirements Specification" and product interface prototype diagram.
- Outline design and detailed design, output conceptual model diagrams (ER diagrams), physical model diagrams, class diagrams, sequence diagrams, etc.
- Coding/Testing.
- Go live/maintenance.
The biggest disadvantage of the waterfall model is that it cannot embrace changes in demand. The product cannot be seen until the entire process is completed, which leads to low team morale.
-
Agile development (Scrum) - product owner, Scrum Master, developers - Sprint
- Product Backlog (user stories, product prototypes).
- Planning meetings (evaluation and budgeting).
- Daily development (stand-up meetings, Pomodoro Technique, pair programming, test first, code refactoring...).
- Fix bugs (problem description, reproduction steps, testers, assignees).
- release version.
- Review meeting (Showcase, users need to participate).
- Retrospective meeting (make a summary of the current iteration cycle).
Supplement: Manifesto for Agile Software Development
- Individuals and Interactions over Processes and Tools
- Working Software Above Thorough Documentation
- Customer Cooperation over Contract Negotiation
- Response to Change higher than Follow Plan
Role: Product owner (the person who decides what to do and can make decisions on requirements), team leader (solves various problems, focuses on how to work better, and shields external influence on the development team), development team (project executive) , specifically developers and testers).
Preparation: business case and funding, contracts, vision, initial product requirements, initial release plan, taking ownership, building a team.
Agile teams usually have 8-10 people.
Workload estimation: Quantify development tasks, including prototypes, Logo design, UI design, front-end development, etc., and try to decompose each work into the minimum task amount. The minimum task amount standard is that the working time cannot exceed two days, and then estimate the overall project time. Post each task on the Kanban board, which is divided into three parts: to do (to be completed), in progress (in progress) and done (completed).
-
-
Project team formation
-
Team composition and roles
Description: Thank you Ms. Fu Xiangying for helping me draw the following beautiful company organizational chart.
-
Programming specifications and code review (
flake8,pylint) -
Some "conventions" in Python (please refer to ["Python Conventions-How to Write Pythonic Code"] (Python Conventions.md))
-
Reasons affecting code readability:
- Too few or no code comments
- Code breaks the best practices of the language
- Anti-pattern programming (spaghetti code, copy-paste programming, ego programming,…)
-
-
Introduction to team development tools
- Version control: Git, Mercury
- Defect management: Gitlab, Redmine
- Agile closed-loop tools: ZenTao, JIRA
- Continuous integration: Jenkins, Travis-CI
Please refer to ["Problems and Solutions in Team Project Development"] (Day91-100/91. Problems and Solutions in Team Project Development.md).
Project topic selection and business understanding
-
Setting the scope of topic selection
-
CMS (client): news aggregation website, Q&A/sharing community, film review/book review website, etc.
-
MIS (user side + management side): KMS, KPI assessment system, HRS, CRM system, supply chain system, warehouse management system, etc.
-
App backend (management terminal + data interface): second-hand transactions, newspapers and magazines, niche e-commerce, news and information, travel, social networking, reading, etc.
-
Other types: own industry background and work experience, business is easy to understand and control.
-
-
Requirement understanding, module division and task allocation
- Requirements understanding: brainstorming and competitive product analysis.
- Module division: Draw a mind map (XMind). Each module is a branch node, and each specific function is a leaf node (expressed with verbs). It is necessary to ensure that each leaf node cannot regenerate new nodes, and determine each Importance, priority and workload of leaf nodes.
- Task allocation: The project leader assigns tasks to each team member based on the above indicators.
-
Develop project schedule (updated daily)
Module Function People Status Completed Work Hours Planned Start Actual Start Planned End Actual End Notes Comment Add comment Wang Dachui Ongoing 50% 4 2018/8/7 2018/8/7 Delete comment Wang Dachui Waiting 0% 2 2018/8/7 2018/8/7 View comments Bai Yuanfang Ongoing 20% 4 2018/8/7 2018/8/7 Code review required Comment voting Bai Yuanfang Waiting 0% 4 2018/8/8 2018/8/8 -
OOAD and database design
-
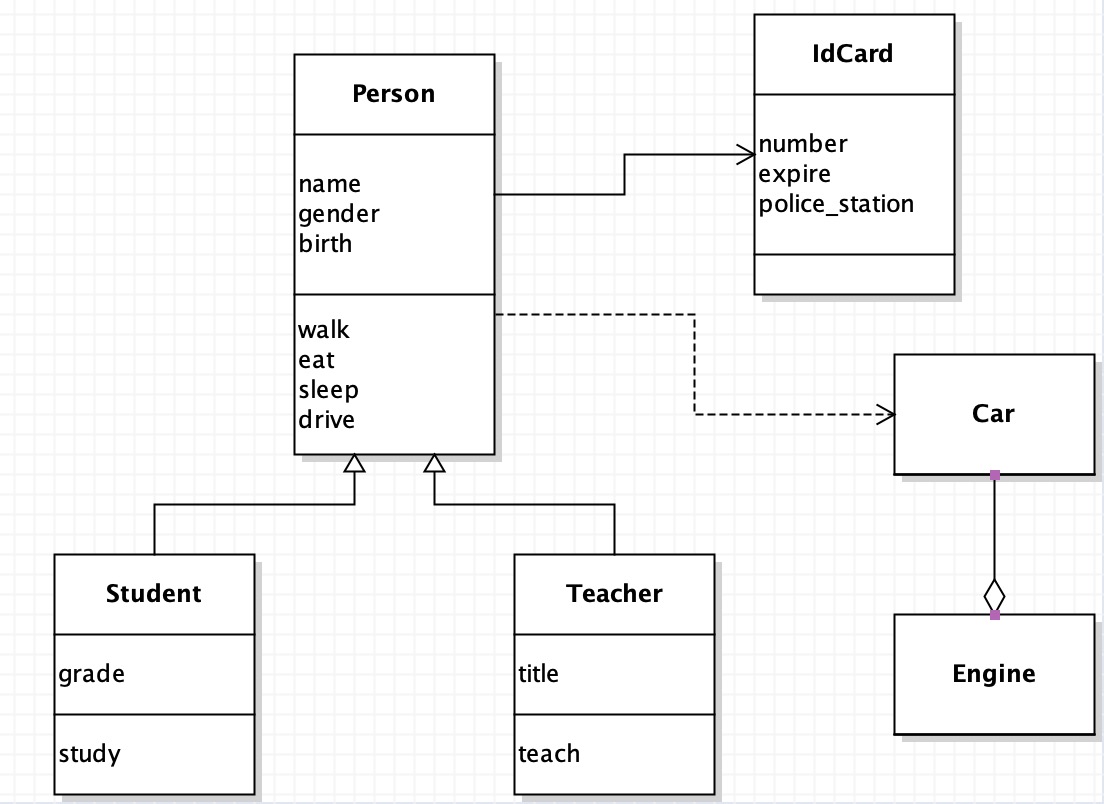
Class diagram of UML (Unified Modeling Language)
-
Create tables through models (forward engineering). For example, in a Django project, you can create a two-dimensional table through the following command.
python manage.py makemigrations app python manage.py migrate -
Use PowerDesigner to draw physical model diagrams.
-
Create a model (reverse engineering) through a data table. For example, in a Django project, you can generate a model through the following command.
python manage.py inspectdb > app/models.py
-
Day 92: [Docker Container Detailed Explanation](./Day91-100/92.Docker Container Detailed Explanation.md)
- Introduction to Docker
- Install Docker
- Use Docker to create containers (Nginx, MySQL, Redis, Gitlab, Jenkins)
- Build Docker image (writing of Dockerfile and related instructions)
- Container orchestration (Docker-compose)
- Cluster management (Kubernetes)
Day 93: [MySQL Performance Optimization](./Day91-100/93.MySQL Performance Optimization.md)
Day 94: [Network API Interface Design](./Day91-100/94.Network API Interface Design.md)
Day 95: [Use Django to develop commercial projects](./Day91-100/95.Use Django to develop commercial projects.md)
Public issues in project development
- Database configuration (multiple databases, master-slave replication, database routing)
- Cache configuration (partition cache, key settings, timeout settings, master-slave replication, failure recovery (Sentinel))
- Log configuration
- Analysis and debugging (Django-Debug-ToolBar)
- Useful Python modules (date calculation, image processing, data encryption, third-party API)
REST API design
- RESTful architecture
- Writing API interface documents
- Application of django-REST-framework
Analysis of key and difficult points in the project
- Use caching to relieve database pressure - Redis
- Use message queues for decoupling and peak clipping - Celery + RabbitMQ
Day 96: [Software testing and automated testing] (Day91-100/96. Software testing and automated testing.md)
unit test
- Types of tests
- Write unit tests (
unittest,pytest,nose2,tox,ddt,...) - Test coverage (
coverage)
Django project deployment
- Preparations before deployment
- Key settings (SECRET_KEY / DEBUG / ALLOWED_HOSTS / cache / database)
- HTTPS/CSRF_COOKIE_SECUR/SESSION_COOKIE_SECURE
- Log related configuration
- Review of common Linux commands
- Installation and configuration of common Linux services
- Use of uWSGI/Gunicorn and Nginx
- Comparison of Gunicorn and uWSGI
- For simple applications that do not require a lot of customization, Gunicorn is a good choice. The learning curve of uWSGI is much steeper than Gunicorn, and Gunicorn's default parameters can already be adapted to most applications.
- uWSGI supports heterogeneous deployment.
- Since Nginx itself supports uWSGI, Nginx and uWSGI are generally deployed together online, and uWSGI is a fully functional and highly customized WSGI middleware.
- In terms of performance, Gunicorn and uWSGI are actually equivalent.
- Comparison of Gunicorn and uWSGI
- Use virtualization technology (Docker) to deploy test environment and production environment
Performance Testing
- Use of AB
- Use of SQLslap
- Use of sysbench
automated test
- Automated testing using Shell and Python
- Use Selenium to implement automated testing
- Selenium IDE
- Selenium WebDriver
- Selenium Remote Control
- Introduction to testing tool Robot Framework
Day 97: [Analysis of technical key points of e-commerce website](./Day91-100/97.Analysis of technical key points of e-commerce website.md)
Day 98: [Project deployment online and performance tuning] (./Day91-100/98. Project deployment online and performance tuning.md)
- MySQL database tuning
- Web server performance optimization
- Nginx load balancing configuration
- Keepalived achieves high availability
- Code performance tuning
- Multithreading
- Asynchronous
- Static resource access optimization
- Cloud storage
- CDN