287 lines
10 KiB
Markdown
287 lines
10 KiB
Markdown
# 挂载根目录导致 device or resource busy
|
||
|
||
## 现象
|
||
|
||
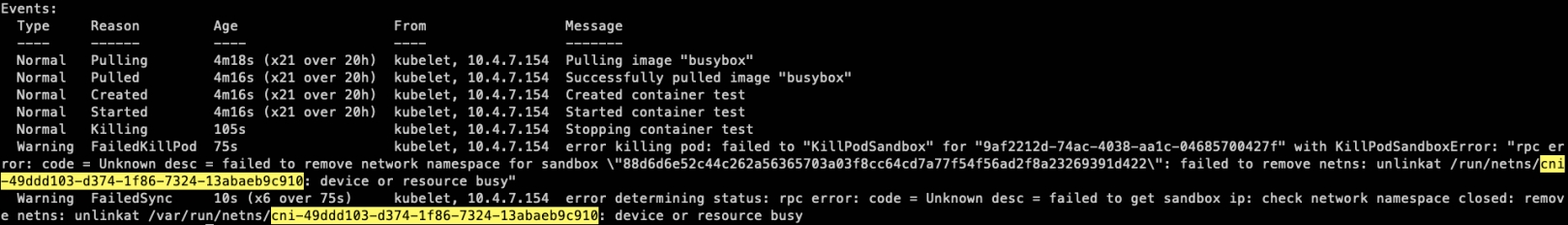
在删除 pod 时,可能会遇到如下事件 `unlinkat xxxxx: device or resource busy`,设备或资源忙导致某个文件无法被删除,进而导致 pod 卡在 Terminating 状态。
|
||
|
||
接下来,就单独针对在 **containerd运行时环境** 下,发生的相关报错进行回顾分析,具体的报错现象如下:
|
||
|
||
```txt
|
||
unlinkat /var/run/netns/cni-49ddd103-d374-1f86-7324-13abaeb9c910: device or resource busy
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
## 复现场景
|
||
|
||
环境:
|
||
|
||
* containerd 运行时
|
||
* centos 7.6 操作系统
|
||
|
||
通过先后创建如下两个服务(sleeping 和 rootfsmount)可以复现问题。
|
||
|
||
1. 先创建 sleeping 服务:
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
$ cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
|
||
apiVersion: apps/v1
|
||
kind: Deployment
|
||
metadata:
|
||
name: sleepping
|
||
spec:
|
||
replicas: 1
|
||
selector:
|
||
matchLabels:
|
||
app: sleepping
|
||
template:
|
||
metadata:
|
||
labels:
|
||
app: sleepping
|
||
spec:
|
||
containers:
|
||
- name: test
|
||
image: busybox
|
||
args: ["sleep", "1h"]
|
||
EOF
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
2. 再创建 rootfsmount 服务,并且保证 pod 实例调度到与 sleeping 服务相同的节点上。
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
$ cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
|
||
apiVersion: apps/v1
|
||
kind: Deployment
|
||
metadata:
|
||
name: rootfsmount
|
||
spec:
|
||
replicas: 1
|
||
selector:
|
||
matchLabels:
|
||
app: rootfsmount
|
||
template:
|
||
metadata:
|
||
labels:
|
||
app: rootfsmount
|
||
spec:
|
||
containers:
|
||
- name: rootfsmount
|
||
image: busybox
|
||
args: ["sleep", "1h"]
|
||
volumeMounts:
|
||
- mountPath: /rootfs
|
||
name: host-rootfs
|
||
volumes:
|
||
- hostPath:
|
||
path: /
|
||
type: ""
|
||
name: host-rootfs
|
||
EOF
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
3. 操作删除 sleeping 服务的 pod,此时可以观察到 pod 实例卡在 Terminating 状态。
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
## 相关知识
|
||
|
||
在进一步了解之前,先熟悉下几个相关知识
|
||
|
||
1. `/run/netns/cni-xxxx` 文件:
|
||
|
||
这个文件实际上就是容器的 net nanemspace 的 mount point,可以通过如下命令进入到容器的 net ns 中:
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
nsenter --net=/var/run/netns/cni-49ddd103-d374-1f86-7324-13abaeb9c910
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
2. Shared subtrees 技术
|
||
|
||
> 此部分为引用说明,详情可见参考链接1
|
||
|
||
* 内核特性,用于控制某个挂载点下的子挂载点是否"传播"给其他挂载点,只应用于 bind mount 和 mount namespace 场景中。
|
||
* Shared subtrees 技术引入了两个概念,分别是 peer group 和 propagation type,接下来一一介绍。
|
||
|
||
2.1 peer group
|
||
|
||
共享挂载信息的一组挂载点,来源主要两种:
|
||
* bind mount,此时源和目的挂载点属于同一 peer group,要求源也是挂载点。
|
||
* 新的 namespace 创建,新的 namespace 会拷贝旧的一份挂载信息,于是,新旧中相同挂载点属于同一 peer group。
|
||
|
||
2.2 propagation type
|
||
|
||
每个挂载点都有这样的一个元数据(propagation type),用于控制当一个挂载点的下面创建和移除挂载点的时候,是否会传播到属于相同peer group的其他挂载点下去,主要有三种:
|
||
|
||
* `MS_SHARED`: 挂载信息在同一个 peer group 里会相互传播。比如把节点上的主目录挂载到容器内的 `/rootfs`,如果节点上的主目录创建了新的挂载点X,则* 在容器内的 `/rootfs` 下面也会出现新的挂载点 `/rootfs/X`。
|
||
* `MS_PRIVATE`:挂载信息在同一个 peer group 里不会相互传播。比如把节点上的主目录挂载到容器内的 `/rootfs`,如果节点上的主目录创建了新的挂载点X,则容器内的 `/rootfs` 下面不会出现新的挂载点 `/rootfs/X`。
|
||
* `MS_SLAVE`:挂载信息传播是单向的。比如把节点上的主目录挂载到容器内的 `/rootfs`,如果节点上的主目录创建了新的挂载点 X,则在容器内的 `/rootfs` 下面也会出现新的挂载点 `/rootfs/X` ,反之则不行。
|
||
|
||
这个对应到 k8s 中 `Container.volumeMounts` 的 `mountPropagation` 字段,分别是:Bidirectional、None、HostToContainer。
|
||
|
||
## 进一步分析
|
||
|
||
让我们再回到复现场景中的第二步,创建 rootfsmount 服务时,发生了什么。
|
||
|
||
通过命令抓取下 contianerd 的所有 mount 系统调用,发现有如下两个 mount 记录:
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
$ strace -f -e trace=mount -p <pid>
|
||
...
|
||
[pid 15532] mount("/", "/run/containerd/io.containerd.runtime.v2.task/k8s.io/5b498caf152857cf1c797761e1f52d64c2ce7d4602b72304da7e154ed31043c8/rootfs/rootfs", 0xc0000f7500, MS_BIND|MS_REC, NULL) = 0
|
||
[pid 15532] mount("", "/run/containerd/io.containerd.runtime.v2.task/k8s.io/5b498caf152857cf1c797761e1f52d64c2ce7d4602b72304da7e154ed31043c8/rootfs/rootfs", 0xc0000f7506, MS_REC|MS_PRIVATE, NULL) = 0
|
||
...
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
这个就对应于 pod 配置中的 volumeMount,我们再进一步看下 container 中的 mount 信息。
|
||
|
||
将节点上的主目录 `/` (挂载点) 挂载到了容器中的 `/rootfs` (挂载点),并且 propagation type 为 rprivate。
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
$ crictl inspect <container-id>
|
||
...
|
||
{
|
||
"destination": "/rootfs",
|
||
"type": "bind",
|
||
"source": "/",
|
||
"options": [
|
||
"rbind",
|
||
"rprivate",
|
||
"rw"
|
||
]
|
||
},
|
||
...
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
让我们再看下pod(或者容器内)的挂载情况:
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
$ cat /proc/self/mountinfo
|
||
...
|
||
# 对应pod的volumeMount设置,将宿主机上的主目录/ 挂载到了容器内的/rootfs目录下
|
||
651 633 253:1 / /rootfs rw,relatime - ext4 /dev/vda1 rw,data=ordered
|
||
695 677 0:3 / /rootfs/run/netns/cni-49ddd103-d374-1f86-7324-13abaeb9c910 rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime - proc proc rw
|
||
...
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
节点上的挂载点(/var/run/netns/cni-49ddd103-d374-1f86-7324-13abaeb9c910)在容器内,也是挂载点(/rootfs/run/netns/cni-49ddd103-d374-1f86-7324-13abaeb9c910)。
|
||
|
||
## 结论
|
||
|
||
当测试服务 rootfsmount 的 pod 实例创建时,会把节点上的主目录 `/` 挂载到容器内(比如 `/rootfs`),由于主目录在节点上是一个挂载点,所以节点上的主目录和容器内的/rootfs属于同一个 peer group,并且采用了默认的 propagation type:rprivate。
|
||
|
||
当测试服务 sleepping 的 pod 实例销毁时,需要解挂和销毁对应的 netns 文件(/var/run/netns/cni-49ddd103-d374-1f86-7324-13abaeb9c910),由于此时的 propagation type 是 rprivate,节点上主目录下的子挂载点解挂不会传递到容器的 net namespace 内,所以,这个 netns 文件(/rootfs/run/netns/cni-49ddd103-d374-1f86-7324-13abaeb9c910)依然是一个挂载点,导致在销毁 netns 文件时会失败。
|
||
|
||
|
||
## 解决方案
|
||
|
||
1. 给 rootfsmount 服务的 volumeMount 配置新增 propagation type,设置为 HostToContainer 或者 Bidirectional。
|
||
|
||
```yaml
|
||
apiVersion: apps/v1
|
||
kind: Deployment
|
||
metadata:
|
||
name: rootfsmount
|
||
spec:
|
||
replicas: 1
|
||
selector:
|
||
matchLabels:
|
||
app: rootfsmount
|
||
template:
|
||
metadata:
|
||
labels:
|
||
app: rootfsmount
|
||
spec:
|
||
containers:
|
||
- name: rootfsmount
|
||
image: busybox
|
||
args: ["sleep", "1h"]
|
||
volumeMounts:
|
||
- mountPath: /rootfs
|
||
name: host-rootfs
|
||
mountPropagation: HostToContainer # 这里显示声明mountPropagation为HostToContainer 或者 Bidirectional
|
||
volumes:
|
||
- hostPath:
|
||
path: /
|
||
type: ""
|
||
name: host-rootfs
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
2. centos 和 redhat 的内核,可以开启如下内核参数:
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
echo 1 > /proc/sys/fs/may_detach_mounts
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
## 疑问:为啥 dockerd 运行时没有这个问题?
|
||
|
||
这里主要有两点:
|
||
|
||
1. dockerd 在启动的时候,开启了内核参数 `fs.may\_detach\_mounts`。
|
||
|
||
```go
|
||
// This is used to allow removal of mountpoints that may be mounted in other
|
||
// namespaces on RHEL based kernels starting from RHEL 7.4.
|
||
// Without this setting, removals on these RHEL based kernels may fail with
|
||
// "device or resource busy".
|
||
// This setting is not available in upstream kernels as it is not configurable,
|
||
// but has been in the upstream kernels since 3.15.
|
||
func setMayDetachMounts() error {
|
||
f, err := os.OpenFile("/proc/sys/fs/may_detach_mounts", os.O_WRONLY, 0)
|
||
if err != nil {
|
||
if os.IsNotExist(err) {
|
||
return nil
|
||
}
|
||
return errors.Wrap(err, "error opening may_detach_mounts kernel config file")
|
||
}
|
||
defer f.Close()
|
||
|
||
_, err = f.WriteString("1")
|
||
if os.IsPermission(err) {
|
||
// Setting may_detach_mounts does not work in an
|
||
// unprivileged container. Ignore the error, but log
|
||
// it if we appear not to be in that situation.
|
||
if !rsystem.RunningInUserNS() {
|
||
logrus.Debugf("Permission denied writing %q to /proc/sys/fs/may_detach_mounts", "1")
|
||
}
|
||
return nil
|
||
}
|
||
return err
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
2. dockerd 在挂载目录时,会验证挂载的源目录与 daemon 的 root 目录的关系,如果源目录是 root 目录的子目录或者 root 目录是源目录的子目录,则将 propagation type 设置为 `MS_SLAVE`。
|
||
|
||
```go
|
||
// validateBindDaemonRoot ensures that if a given mountpoint's source is within
|
||
// the daemon root path, that the propagation is setup to prevent a container
|
||
// from holding private refereneces to a mount within the daemon root, which
|
||
// can cause issues when the daemon attempts to remove the mountpoint.
|
||
func (daemon *Daemon) validateBindDaemonRoot(m mount.Mount) (bool, error) {
|
||
if m.Type != mount.TypeBind {
|
||
return false, nil
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// check if the source is within the daemon root, or if the daemon root is within the source
|
||
if !strings.HasPrefix(m.Source, daemon.root) && !strings.HasPrefix(daemon.root, m.Source) {
|
||
return false, nil
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
if m.BindOptions == nil {
|
||
return true, nil
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
switch m.BindOptions.Propagation {
|
||
case mount.PropagationRSlave, mount.PropagationRShared, "":
|
||
return m.BindOptions.Propagation == "", nil
|
||
default:
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
return false, errdefs.InvalidParameter(errors.Errorf(`invalid mount config: must use either propagation mode "rslave" or "rshared" when mount source is within the daemon root, daemon root: %q, bind mount source: %q, propagation: %q`, daemon.root, m.Source, m.BindOptions.Propagation))
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
## 参考文档
|
||
|
||
* [Shared subtree](https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000006899213)
|
||
* [Mount Propagation](https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/concepts/storage/volumes/#mount-propagation)
|