Label
Label 是附着到 object 上(例如 Pod)的键值对。可以在创建 object 的时候指定,也可以在 object 创建后随时指定。Labels 的值对系统本身并没有什么含义,只是对用户才有意义。
"labels": {
"key1" : "value1",
"key2" : "value2"
}
Kubernetes 最终将对 labels 最终索引和反向索引用来优化查询和 watch,在 UI 和命令行中会对它们排序。不要在 label 中使用大型、非标识的结构化数据,记录这样的数据应该用 annotation。
动机
Label 能够将组织架构映射到系统架构上(就像是康威定律),这样能够更便于微服务的管理,你可以给 object 打上如下类型的 label:
"release" : "stable","release" : "canary""environment" : "dev","environment" : "qa","environment" : "production""tier" : "frontend","tier" : "backend","tier" : "cache""partition" : "customerA","partition" : "customerB""track" : "daily","track" : "weekly""team" : "teamA","team:" : "teamB"
语法和字符集
Label key 的组成:
- 不得超过 63 个字符
- 可以使用前缀,使用 / 分隔,前缀必须是 DNS 子域,不得超过 253 个字符,系统中的自动化组件创建的 label 必须指定前缀,
kubernetes.io/由 kubernetes 保留 - 起始必须是字母(大小写都可以)或数字,中间可以有连字符、下划线和点
Label value 的组成:
- 不得超过 63 个字符
- 起始必须是字母(大小写都可以)或数字,中间可以有连字符、下划线和点
Label selector
Label 不是唯一的,很多 object 可能有相同的 label。
通过 label selector,客户端/用户可以指定一个 object 集合,通过 label selector 对 object 的集合进行操作。
Label selector 有两种类型:
- equality-based :可以使用
=、==、!=操作符,可以使用逗号分隔多个表达式 - set-based :可以使用
in、notin、!操作符,另外还可以没有操作符,直接写出某个 label 的 key,表示过滤有某个 key 的 object 而不管该 key 的 value 是何值,!表示没有该 label 的 object
示例
$ kubectl get pods -l environment=production,tier=frontend
$ kubectl get pods -l 'environment in (production),tier in (frontend)'
$ kubectl get pods -l 'environment in (production, qa)'
$ kubectl get pods -l 'environment,environment notin (frontend)'
在 API object 中设置 label selector
在 service、replicationcontroller 等 object 中有对 pod 的 label selector,使用方法只能使用等于操作,例如:
selector:
component: redis
在 Job、Deployment、ReplicaSet 和 DaemonSet 这些 object 中,支持 set-based 的过滤,例如:
selector:
matchLabels:
component: redis
matchExpressions:
- {key: tier, operator: In, values: [cache]}
- {key: environment, operator: NotIn, values: [dev]}
如 Service 通过 label selector 将同一类型的 pod 作为一个服务 expose 出来。
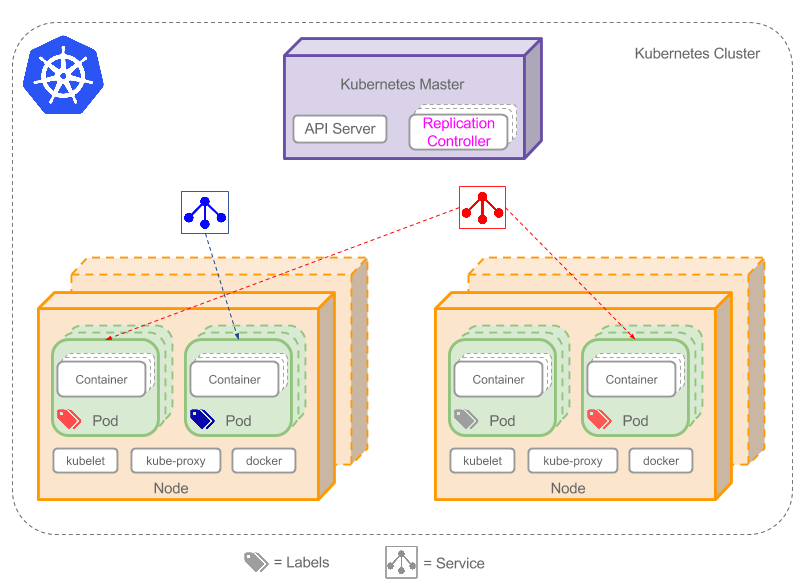
另外在 node affinity 和 pod affinity 中的 label selector 的语法又有些许不同,示例如下:
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: kubernetes.io/e2e-az-name
operator: In
values:
- e2e-az1
- e2e-az2
preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- weight: 1
preference:
matchExpressions:
- key: another-node-label-key
operator: In
values:
- another-node-label-value